 |
 |
- Search
| Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab > Volume 24(1); 2019 > Article |
|
Abstract
Purpose
Methods
Results
Notes
Supplementary material
Fig. 1.
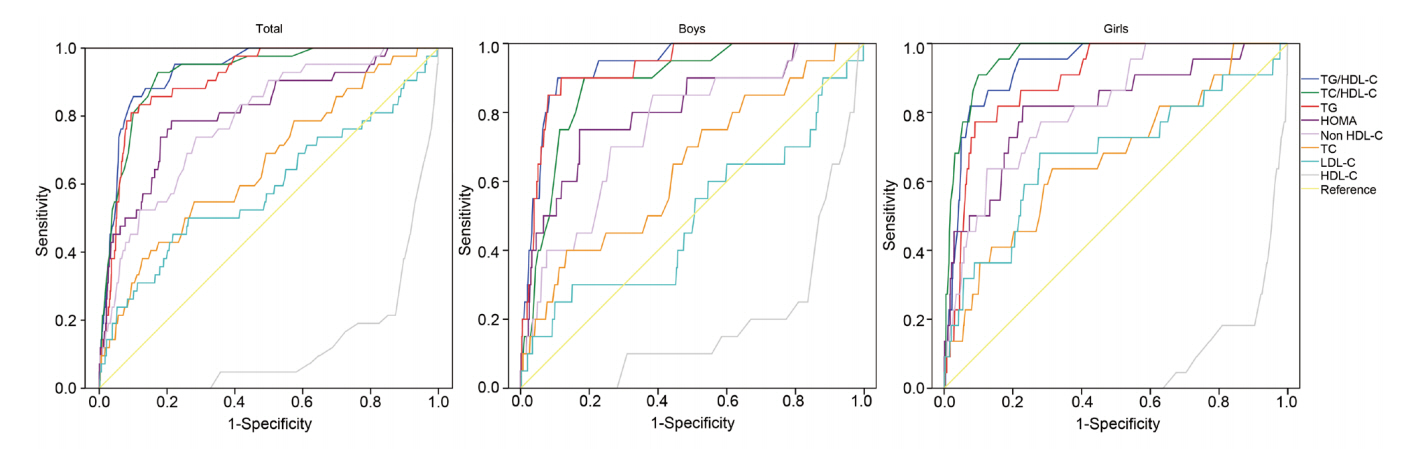
Fig. 2.
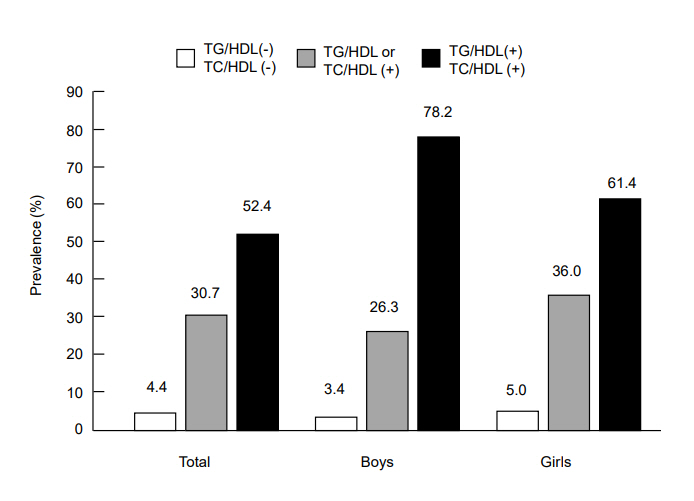
Fig. 3.
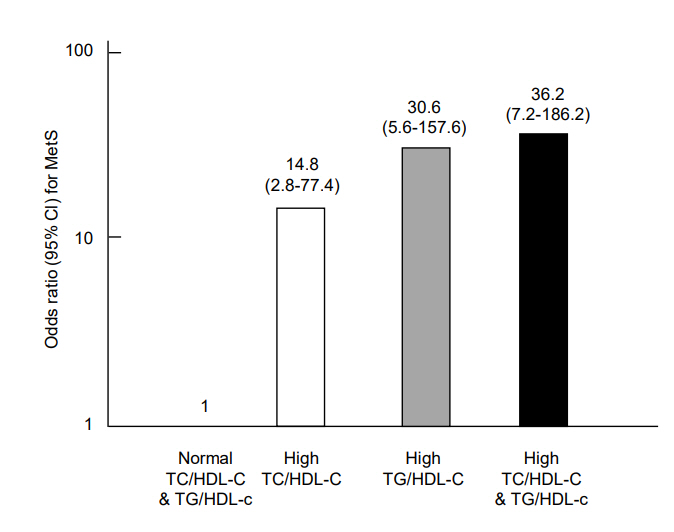
Table 1.
Values are presented as mean (geometric geometric mean for lipid parameters)±standard error or number (%).
Metabolic syndrome was defined using International Diabetes Federation criteria.
BMI, body mass index; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HOMA-IR, homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; TC, total cholesterol; TG, triglyceride; WC, waist circumference.
Table 2.
| Variable |
Boys |
Girls |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geometric mean (95% CI) | 5th | 10th | 90th | 95th | Geometric mean (95% CI) | 5th | 10th | 90th | 95th | |
| TC (mg/dL) | ||||||||||
| Total | 152.5 (150.6–154.4) | 115 | 124 | 192 | 204 | 159.9 (158.3–161.6) | 124 | 132 | 196 | 207 |
| 10–12 yr | 161.9 (159.2–164.6)** | 124 | 132 | 198 | 210 | 160.1 (157.7–162.6) | 127 | 133 | 192 | 201 |
| 13–15 yr | 147.9 (145.1–150.8) | 112 | 120 | 181 | 197 | 158.7 (156.1–161.3) | 121 | 129 | 198 | 208 |
| 16–18 yr† | 148.4 (145.7–151.2) | 110 | 120 | 185 | 197 | 161.1 (158.0–164.3) | 125 | 132 | 200 | 209 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | ||||||||||
| Total | 74.9 (72.2–77.7) | 34 | 39 | 147 | 186 | 77.9 (75.5–80.3) | 37 | 44 | 146 | 174 |
| 10–12 yr | 70.6 (66.7–74.7)** | 31 | 37 | 142 | 184 | 86.5 (82.4–90.9)** | 36 | 45 | 152 | 183 |
| 13–15 yr | 75.0 (70.6–79.7) | 34 | 40 | 148 | 197 | 77.8 (73.7–82.1)** | 38 | 45 | 145 | 181 |
| 16–18 yr† | 79.0 (74.6–83.7) | 37 | 42 | 152 | 186 | 70.7 (67.5–74.1) | 37 | 41 | 127 | 160 |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | ||||||||||
| Total | 47.6 (47.1–48.2) | 35 | 37 | 62 | 66 | 50.0 (49.4–50.6) | 36 | 39 | 63 | 67 |
| 10–12 yr | 50.5 (49.5–51.5)** | 36 | 39 | 65 | 70 | 49.7 (48.8–50.6) | 36 | 39 | 63 | 68 |
| 13–15 yr | 46.4 (45.7–47.2) | 35 | 36 | 59 | 63 | 49.4 (48.3–50.6) | 36 | 39 | 62 | 66 |
| 16–18 yr† | 46.1 (45.2–47.0) | 34 | 36 | 57 | 63 | 50.9 (49.8–52.0) | 37 | 39 | 64 | 68 |
| LDL-C (mg/dL) | ||||||||||
| Total | 85.8 (84.1–87.5) | 55 | 63 | 119 | 130 | 91.0 (89.5–92.5) | 61 | 68 | 123 | 133 |
| 10–12 yr | 93.3 (91.1–95.6)** | 60 | 69 | 126 | 138 | 89.4 (87.2–91.7)* | 57 | 67 | 119 | 128 |
| 13–15 yr | 82.2 (79.9–84.6) | 54 | 60 | 112 | 122 | 90.3 (88.0–92.6) | 61 | 67 | 123 | 134 |
| 16–18 yr† | 82.5 (79.9–85.2) | 48 | 59 | 117 | 127 | 93.2 (90.6–96.0) | 64 | 69 | 128 | 140 |
| Non-HDL-C (mg/dL) | ||||||||||
| Total | 103.2 (101.4–105.0) | 69 | 77 | 141 | 153 | 108.4 (106.9–110.0) | 76 | 82 | 143 | 156 |
| 10–12 yr | 109.7 (107.3–112.2)** | 77 | 82 | 148 | 158 | 108.9 (106.6–111.3) | 75 | 84 | 141 | 150 |
| 13–15 yr | 99.8 (96.9–102.7) | 68 | 75 | 135 | 149 | 108.0 (105.6–110.4) | 76 | 81 | 143 | 160 |
| 16–18 yr† | 100.6 (98.0–103.4) | 65 | 73 | 139 | 154 | 108.6 (105.6–111.6) | 76 | 81 | 147 | 159 |
| TC/HDL-C ratio | ||||||||||
| Total | 3.2 (3.1–3.3) | 2.3 | 2.4 | 4.3 | 4.7 | 3.2 (3.1–3.3) | 2.4 | 2.5 | 4.1 | 4.6 |
| 10–12 yr | 3.2 (3.1–3.3) | 2.3 | 2.4 | 4.2 | 4.5 | 3.2 (3.1–3.3) | 2.3 | 2.5 | 4.2 | 4.6 |
| 13–15 yr | 3.2 (3.1–3.3) | 2.3 | 2.5 | 4.3 | 4.7 | 3.2 (3.1–3.3) | 2.4 | 2.5 | 4 | 4.6 |
| 16–18 yr† | 3.2 (3.1–3.3) | 2.3 | 2.4 | 4.5 | 5 | 3.2 (3.1–3.3) | 2.4 | 2.5 | 4.3 | 4.7 |
| TG/HDL-C ratio | ||||||||||
| Total | 1.6 (1.5–1.7) | 0.6 | 0.7 | 3.5 | 4.5 | 1.6 (1.5–1.7) | 0.7 | 0.8 | 3.3 | 4.3 |
| 10–12 yr | 1.4 (1.3–1.5)** | 0.5 | 0.6 | 3.4 | 4.4 | 1.7 (1.6–1.8)** | 0.6 | 0.8 | 3.5 | 4.6 |
| 13–15 yr | 1.6 (1.5–1.7) | 0.6 | 0.7 | 3.4 | 5.1 | 1.6 (1.5–1.7)** | 0.7 | 0.8 | 3.2 | 4.3 |
| 16–18 yr† | 1.7 (1.6–1.8) | 0.7 | 0.9 | 3.8 | 4.5 | 1.4 (1.3–1.5) | 0.6 | 0.7 | 2.9 | 3.7 |
Table 3.
AUCROC, area under the curve of the receiver operating characteristic; HOMA-IR, homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance; HDL-C, highdensity lipoprotein cholesterol; SE, standard error; TC/HDL-C, total cholesterol to high density lipoprotein cholesterol; TG/HDL-C, triglyceride to high density lipoprotein cholesterol.
References
- TOOLS
- Related articles in APEM







