 |
 |
- Search
| Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab > Volume 26(2); 2021 > Article |
|
Abstract
Purpose
We sought to evaluate features of partial remission (PR) in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) using the insulin-dose adjusted A1c (IDAA1c) definition and to identify risk factors associated with nonremission.
Methods
Medical records of patients with newly diagnosed T1DM between January 1, 2008, and June 30, 2018, were retrospectively reviewed. Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) readings and insulin total daily doses (TDDs) of each patient at each follow-up visit were obtained with IDAA1c values calculated. PR was defined as an IDAA1c score of 9 points or less within 6 months of diagnosis. The trends of HbA1c and TDD within 2 years after diagnosis were compared between remitters and nonremitters. Factors that may predict the occurrence of PR were studied, with their relative risks of nonremission calculated.
Results
PR occurred in 26 patients (45.6%), including 8 girls and 18 boys, with a median duration of 8 months. The frequency of remission in male patients was significantly higher (P=0.002) and the relative risk of female sex with nonremission was 2.20 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.24–3.91), which remained significant when adjusted by multivariate regression modeling. The initial HbA1c level at diagnosis was also significantly higher in the nonremission group (P=0.029), with a relative risk of 1.12 (95% CI, 1.01–1.25). Both HbA1c (P=0.012) and TDD (P=0.006) were significantly lower within 2 years after diagnosis among remitters than in nonremitters. TDD was significantly lower in male patients (P=0.029) during the same period, while there was no significant difference in HbA1c level between male and female patients (P=0.163).
Initial HbA1c level at diagnosis and sex are factors associated with the occurrence of partial remission, as defined by the insulin-dose adjusted A1c criteria, in children with type 1 diabetes. Female sex is an independent risk factor of nonremission likely resulting from a higher insulin requirement.
Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) is one of the most common chronic illnesses in childhood that results from the autoimmune destruction of β-cells. Many children who are diagnosed with T1DM experience a phase called a "honeymoon period" or "partial remission" (PR) shortly after the initiation of insulin therapy, which is characterized by a significant reduction in insulin requirement while maintaining good glycemic control. Cases of children with a period of exogenous insulin independence have also been observed [1-3]. The frequency of PR in children varies in different studies, with a range of 25% to 100% [1]. This wide range is partly due to the use of different definitions of PR between studies. In 2009, Mortensen et al. [4] proposed a new formula to incorporate the hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) value and daily insulin requirement to standardize the definition of PR, which is referred to as the "insulin dose-adjusted HbA1c" (IDAA1c) [4]. A value of 9 points or less indicates PR as this value correlates with a stimulated C-peptide level of greater than 300 pmol/L, which is in line with the Diabetes Control and Complication Trial definition of a "C-peptide responder." [5] This formula has been validated to date in large cohorts of pediatric T1DM patients and demonstrated a satisfactory correlation with residual β-cell functions [6]. Since then, IDAA1c has been adopted as the definition of PR in different studies and is now largely considered the gold standard criterion for PR.
Ever since the 1970s, studies of patients with T1DM have been conducted in an attempt to search for methods to preserve residual β-cell functions, assessing the use of immunomodulatory drugs such as cyclosporin A [7], steroids and azathioprine [8], or even plasmapheresis [9]. Unfortunately, the efficacy results of these drugs did not justify their use in clinical practice. With increasing evidence showing that patients in the remitter group were associated with better metabolic control and a lower long-term complication risk [10-13], together with a growing pool of knowledge regarding the autoimmunity process of T1DM on a molecular level in recent decades [14], the PR phase is once again gaining scientific interest among researchers. The pathophysiology and mechanism that bring about the transient PR phase are far from being clearly understood at present. Studies on this peculiar phase of T1DM can potentially provide valuable insight into the development of management strategies tailored to remitters and nonremitters, respectively. Besides, the identification of both remitters and nonremitters would be helpful clinically. For example, nonremitters may require more stringent insulin therapy soon after their diagnosis and an even greater emphasis on complication prevention. It may also help to detect patients existing in the PR phase and facilitate better titration of insulin treatment to maintain good glycemic control.
While a number of studies have been published so far looking into factors that may predict the occurrence of PR using different definitions, they have offered diverging results. The aim of this study was to describe the features of PR using the definition of IDAA1c in concert with our local data and to identify risk factors associated with nonremission.
Medical records of patients who presented to the Department of Pediatrics of Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Hong Kong, with newly diagnosed T1DM during the period of January 1, 2008, to June 30, 2018, were retrospectively reviewed. The diagnosis of T1DM was reviewed and established using a fasting blood glucose concentration of at least 7 mmol/L and/or random blood glucose concentration of at least 11mmol/L, along with symptoms of polyuria and/or polydipsia as well as the presence of diabetes-associated autoantibodies. However, limited by the fact that only one type of autoantibody, anti-islet cell antibodies (AICAs), was available for testing in public hospitals of Hong Kong at the time of this study, the diagnosis of T1DM was only established in the absence of obesity (defined as body mass index ≥25 kg/m2), absence of a first-degree family history of early-onset diabetes (<30 years old), and the presence of significant ketosis at diagnosis in those who tested negative for AICAs.
Demographic data and clinical characteristics were extracted from patient medical records, including sex, age at diagnosis, ethnicity, pubertal status, body mass index at diagnosis, and the presence of concomitant infection as evident by a positive finding of sepsis screening at presentation. Laboratory results at diagnosis were also reviewed from the clinical management system and medical notes, including serum pH, serum bicarbonate, base excess, initial blood glucose, HbA1c, and the presence of AICAs. Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) was defined as follows: serum glucose level of greater than 11 mmol/L, a serum pH of less than 7.3 or serum bicarbonate level of less than 15 mmol/L, and the presence of ketonemia with a β-hydroxybutyric acid level of at least 3 mmol/L or a moderate to large ketonuria. The severity of DKA was further classified as mild (pH, 7.20–7.29 or serum bicarbonate <15 mmol/L), moderate (pH, 7.10–7.19), or severe (pH <7.10) [15]. During subsequent follow-up assessments, the insulin dosages, body weight, and HbA1c values of each patient were used to calculate the IDAA1c value, using the formula HbA1c (%)+4×(total daily dose [TDD] in unit/kg/day) [4]. A patient was classified as having PR if their IDAA1c value was 9 points or less at within the first 6 months of diagnosis. Patients who were lost to follow-up within 6 months of their diagnosis were excluded from this study as there was not enough information available in these cases to confirm the presence or absence of PR.
Descriptive data were expressed as either median (interquartile range) or frequency (percentage) values. Pearson chi-square test or Fisher exact test was used for comparisons between categorical variables. Continuous variables had their normality tested by a graphical method. Log transformation was attempted for nonnormally distributed variables. Variables were then compared by a t-test (if normally distributed) or the Mann-Whitney U-test (if not normally distributed). The risk of nonremission contributed to by the potential variables was assessed by assessing the relative risk using the log-binomial regression model, and all significant variables in the univariate analysis were entered into a multivariate log-binomial regression. In the case of nonconvergence in the multivariate log-binomial regression model, modified Poisson regression was applied. Results were expressed as relative risk values with 95% CIs. Besides, the trends in HbA1c and insulin TDD within 2 years after the diagnosis of T1DM were studied. The differences in HbA1c and TDD over the examined period were analyzed using a generalized estimating equations model. Statistical analysis was performed using the IBM SPSS Statistics ver. 22.0 (IBM Co., Armonk, NY, USA), and a P-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
A total of 57 patients (30 girls and 27 boys) aged 18 months to 18 years at diagnosis were enrolled. Nine patients were referred to our department after diagnosis and 48 patients were presented to us directly via the emergency department. Thirty-seven patients (66.1%) presented with DKA at diagnosis, including 2 patients who had a record of the presence of DKA but no details regarding its severity. None of the patients had experienced complete remission. PR occurred in 26 patients (45.6%), including 8 girls and 18 boys, with a median duration of 8 months. Other clinical and laboratory characteristics at diagnosis are given in Table 1.
The frequency of remission in male patients was significantly higher (66.7% in boys vs. 26.7% in girls, P=0.002) and the relative risk of girls for nonremission was 2.20 (95% CI, 1.24–3.91). Remitters were also found to have significantly lower HbA1c levels at diagnosis as compared with nonremitters (median [interquartile range]: 12.5% [2.6%] vs. 14.2% [3.6%], P=0.029). The relative risk of HbA1c at diagnosis for nonremission was 1.12 (95% CI, 1.01–1.25). (Tables 2 and 3, Supplementary Table 1). When the 2 factors were adjusted using the multivariate regression model, female sex remained a significant independent risk factor for nonremission (relative risk, 2.38; 95% CI, 1.35–4.20). (Table 3, Supplementary Table 2) There was a significantly greater proportion of male patients who presented in a prepubertal status (63%) relative to female patients (36.7%) in our cohort (P=0.032); however, prepuberty was not a statistically significant variable associated with PR on its own (P=0.179).
The trends in HbA1c and TDD in this cohort over a period of 2 years after the diagnosis of T1DM are presented in Fig. 1. One to 3 months after diagnosis, patients reached their lowest median HbA1c level of 7%, which then increased to a median of 8% by 4 to 6 months and thereafter stabilized at a range of 7.7% to 8.45% until 22 to 24 months after diagnosis. The overall TDD also dropped to a median of 0.635 unit/kg/day by 1 to 3 months after diagnosis, but subsequently adopted a stable, increasing trend from 4 to 6 months, then increased up to 0.782 unit/kg/day by 22 to 24 months. The trends in HbA1c and TDD in remitters versus nonremitters and male versus female patients from onset to 24 months after diagnosis are shown in Fig. 2A and B. Both HbA1c (P=0.012) and TDD (P=0.006) were significantly lower during this time period in remitters than in nonremitters, but the differences between the 2 groups gradually diminished with increasing time after diagnosis. When comparing patients of both sexes, TDD was significantly lower in male patients (P=0.029) but the HbA1c level did not significantly differ between male and female patients during the study follow-up period (P=0.163).
In this study, the frequency of PR in our cohort was 45.6%. This number is comparable to that reported by other published studies that also defined PR using the IDAA1c criteria (range, 35%–71.1%) [16-21]. IDAA1c is an easy-to-use formula in a clinic setting that gives reasonable sensitivity and specificity in identifying PR status and guiding management planning. However, it has not yet been validated in patients using insulin pumps who often require lower TDDs relative to patients receiving multiple daily injections. Recently, a study has proposed the use of a TDD of less than 0.3 unit/kg/day as a more straightforward and user-friendly definition of PR and concluded this criterion is noninferior to IDAA1c [18]. Nonetheless, when we tried to apply this definition to our cohort, only five of 57 total patients (8.8%) could be classified into the PR group, which was drastically discrepant from the result when using the IDAA1c definition. We postulate that ethnicity could be one of the reasons for this discrepancy, as it is known to influence insulin sensitivity and response [22,23]. Using the TDD of less than 0.3 unit/kg/day definition might demonstrate a lower sensitivity in the Asian population and therefore would not be applicable in our locality. Meanwhile, a more recent study published in 2018 proposed another definition for PR, referred to as the glycemic target-adjusted HbA1c [21], but more research is required for its validation, including its applicability in populations similar to our study cohort.
Most patients experience a drop in both HbA1c level and insulin requirements regardless of the presence of PR soon after their diagnosis of T1DM and initiation of insulin therapy, although the PR group experienced a significantly greater decrement in both aspects. Two other studies also have demonstrated a similar trend [20,24]. This observation supports the theory that the initiation of exogenous insulin therapy in newly diagnosed T1DM patients allows β-cell rest and reversal of glucotoxicity and, hence, the recovery of insulin synthesis and the secretion of variable magnitudes. Several pathways had been proposed in various studies that might account for the mechanism of glucotoxicity [25]. It has also been suggested that the longer duration of preceding chronic hyperglycemia and the smaller β-cell recovery potential ultimately reach the point of irreversibility [26]. This ties in with our finding of a lower initial HbA1c level at diagnosis, reflecting the idea a reduced level or shorter duration of preceding glucotoxicity was associated with a higher occurrence of PR due to the greater reversibility of β-cell functions, although statistical significance was found in the univariate but not the multivariate analysis, which could possibly be limited by our small sample size. Similar findings of a relationship between the initial HbA1c level at diagnosis and PR were described by 2 other studies [20,27]. Besides, the immunological response might also play a role in the development of PR. It was hypothesized that the transient restoration of immune tolerance to β-cells might result in recovery in its function [25,28]. Overall, the PR phase is likely to be contributed by a combination of metabolic and immunologic mechanisms.
On the other hand, patients in this study showed an overall trend of reaching the trough HbA1c level and TDD by 1 to 3 months after diagnosis, which was followed by a gradual increase in both parameters subsequently. This suggests any interventional studies aiming to prolong endogenous β-cell function should recruit patients soon after their diagnosis and start the intervention preferably within 3 months of diagnosis in order to maximize β-cell preservation. Also, we observed a gradual diminishment of the median A1c difference between the PR and non-PR groups over time after diagnosis. Similar findings were observed in other studies as well [18,19]. This might suggest that the presence of PR might not affect the level of HbA1c in the long run.
We found significantly more male patients went into PR than female ones and sex was an independent factor for PR occurrence. This finding was in concordance with those of several other studies [3,17,18,20,27]. There was also a study that reported a more severe degree of disease in girls at diagnosis and a sex difference in the frequencies of different T1DM autoantibodies; specifically, a greater frequency of glutamic acid decarboxylase autoantibodies in girls was observed, whereas boys more commonly tested positive for insulin autoantibodies, islet antigen-2 antibodies, and zinc transporter 8 antibodies [29]. Such differences in autoantibody profile might contribute to variable autoimmune destruction of islet cells, hence causing different disease courses, severities, and frequencies of PR.
A number of studies have reported that female T1DM patients in general require more exogenous insulin than male patients [30,31], and this phenomenon can be observed across all pediatric age groups, including young children less than 5 years of age [32]. Therefore, it could not solely be explained by differences in sex hormone secretions, physical activity level, or body compositions related to pubertal changes. Our study offered a similar finding of a significantly higher average TDD within the first 2 years after diagnosis in girls without a significant difference in HbA1c level during the same period between the sexes. On the contrary, other studies have failed to observe a sex difference in the stimulated C-peptide level of patients at diagnosis [4,30]. As a result, whether the higher exogenous insulin requirement in girls translates to a lower residual β-cell function or merely represents a higher degree of insulin resistance remains unclear. In the case of insulin resistance, the IDAA1c would not be able to accurately reflect the residual β-cell function in girls as the equation is unable to discriminate between insulin secretion and insulin resistance. A sex-specific cutoff value for IDAA1c might need to be explored in order to support clinical application of this factor.
Previous studies have offered diverging findings regarding the effect of age of onset on the occurrence of PR. This could partly be explained by the different age groupings used in different studies. In this present study, we did not identify the age of onset as a factor influencing PR. We were unable to further stratify patients into different age groups for analysis due to the small sample size. However, in general, more studies have suggested that an older age of onset is associated with a greater chance of PR, especially when compared to the group of those younger than 5 years of age [1,4,17,20,21,27,33]. In particular, prepubertal children older than 5 years of age appeared to have the greatest likelihood of PR. There were several postulations of why very young children often do not enter into PR. The most commonly quoted reason was that young infants are unable to verbalize their symptoms, so they are usually diagnosed at a later stage of disease. This was supported by studies reporting a higher percentage of DKA in this age group [33,34]. Second, from evidence of counting β-cells in autopsies of individuals without diabetes, children have less β-cells than adults and it is believed that adult β-cell mass is not reached until early adolescence [35]. Third, studies have shown a faster decline in C-peptide level in very young patients, which might represent a more aggressive disease course in this population [35,36].
On the other end of the spectrum, older patients undergoing puberty at diagnosis seemed to be associated with nonremission as well, as reported in 2 studies [3,37]. Puberty is associated with nonremission due to an increase in counter-regulatory hormones—in particular, growth hormone—hence resulting in insulin insensitivity [31]. In this study, prepubertal status at diagnosis was associated with more frequent PR, but not to a statistically significant degree. This result could be due to the fact that pubertal staging was performed by different attending doctors, which might have caused interrater variation.
The major limitation of our study was its small sample size. Also, there were no available data of C-peptide values of individual patients for correlation. Fasting or stimulated C-peptide testing was not supported by our laboratory service in the past. Furthermore, insulin dosages were retrieved from computer dispensing records and did not account for correction boluses or noncompliance. Attempts were made to countercheck the actual insulin dosage given by reviewing the consultation notes of patients’ clinic visits, which documented any reported self-titration of insulin dose. In addition, our patients with newly diagnosed T1DM did not have their HbA1c level checked at the same time points after diagnosis as there was no standardized schedule for blood-taking during follow-up, which resulted in occasional missing data of HbA1c levels, although the majority of patients had at least one HbA1c reading per 3-month interval up to 2 years after diagnosis.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study on the PR status of T1DM in the Chinese population using the definition of IDAA1c. Based on our results, we concluded that both initial HbA1c level at diagnosis and sex are factors associated with the occurrence of PR. Female sex was an independent risk factor of nonremission, likely resulting from a higher insulin requirement among female T1DM patients than male patients. More research is necessary to delineate the pathogenesis of PR and its clinical implications in the treatment of T1DM.
Notes
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Tables 1 and 2 can be found via https://doi.org/apem.2040202.101.
Supplementary Table 1.
Univariate regression model for assessing relative risk for nonremission
Supplementary Table 2.
Multivariate regression model for assessing relative risk for nonremission
Fig. 1.
Median hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) level and total daily dose (TDD) over a period of 2 years after the onset of T1DM. The dotted lines represent the 25th and 75th percentiles.
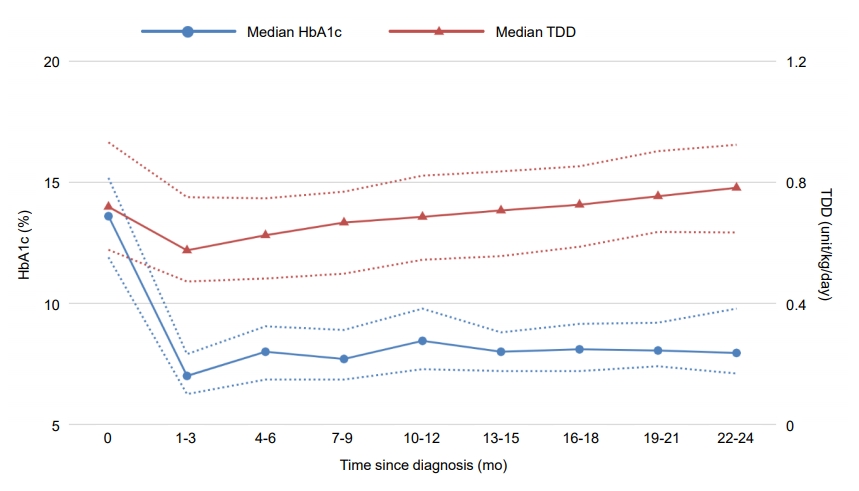
Fig. 2.
(A) Change in hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) level and total daily dose (TDD) over time, stratified by partial remission (PR) status. Both the HbA1c level and TDD were significantly less over this period in patients with PR than in those without PR. (B) Change in HbA1c level and TDD over time, stratified by sex. TDD is significantly different between the 2 groups, with a P-value of 0.029; the HbA1c level is not (P=0.163).

Table 1.
Baseline demographics and clinical features of the study cohort (n=57)
Table 2.
Clinical characteristics of patients in each group
| Variable | PR (n=26) | No PR (n=31) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age at diagnosis (yr), median (IQR) | 9.5 (7) | 10 (8) | 0.766 |
| Female sex, median (IQR) | 8 (30.8) | 22 (71.0) | 0.002* |
| Chinese ethnicity | 21 (80.8) | 26 (83.9) | 0.759 |
| Follow-up period (mo), median (IQR) | 45 (30) | 63 (30) | 0.396 |
| Switch from MDI to insulin pump | 6 (23.1) | 2 (6.5) | 0.124 |
| BMI at diagnosis (kg/m2), median (IQR) | 15.2 (3.5) | 15.8 (4.8) | 0.707 |
| Prepubertal | 15 (60) | 13 (41.9) | 0.179 |
| Presence of DKA at diagnosis | 17 (65.4) | 20 (66.7) | 0.920 |
| HbA1c at diagnosis (%), median (IQR) | 12.5 (2.6) | 14.2 (3.6) | 0.029* |
| Serum glucose at diagnosis (mmol/L), median (IQR) | 24.7 (17.5) | 26 (13.5) | 0.798 |
| pH at diagnosis, median (IQR) | 7.26 (0.22) | 7.22 (0.26) | 0.585 |
| Serum HCO3- at diagnosis (mmol/L), median (IQR) | 13.0 (15.2) | 10.7 (15.1) | 0.806 |
| Presence of AICA | 20 (76.9) | 20 (64.5) | 0.308 |
| Concomitant infection | 3 (12) | 2 (6.9) | 0.653 |
| Insulin dose on discharge (unit/kg/day), median (IQR) | 0.61 (0.34) | 0.78 (0.39) | 0.083 |
Table 3.
Relative risk of individual variables for nonremission
References
1. Abdul-Rasoul M, Habib H, Al-Khouly M. "The honeymoon phase" in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus: frequency, duration, and influential factors. Pediatr Diabetes 2006;7:101–7.


2. Böber E, Dündar B, Büyükgebiz A. Partial remission phase and metabolic control in type 1 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 2001;14:435–41.


3. Kara Ö, Esen İ, Tepe D. Factors influencing frequency and duration of remission in children and adolescents newly diagnosed with type 1 diabetes. Med Sci Monit 2018;24:5996–6001.



4. Mortensen HB, Hougaard P, Swift P, Hansen L, Holl RW, Hoey H, et al. New definition for the partial remission period in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009;32:1384–90.



5. Effect of intensive therapy on residual beta-cell function in patients with type 1 diabetes in the diabetes control and complications trial. A randomized, controlled trial. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. Ann Intern Med 1998;128:517–23.


6. Max Andersen MLC, Hougaard P, Pörksen S, Nielsen LB, Fredheim S, Svensson J, et al. Partial remission definition: validation based on the insulin dose-adjusted HbA1c (IDAA1C) in 129 Danish Children with New-Onset Type 1 Diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes 2014;15:469–76.


7. Assan R, Feutren G, Debray-Sachs M, Quiniou-Debrie MC, Laborie C, Thomas G, et al. Metabolic and immunological effects of cyclosporin in recently diagnosed type 1 diabetes mellitus. Lancet 1985;1:67–71.


8. Silverstein J, Maclaren N, Riley W, Spillar R, Radjenovic D, Johnson S. Immunosuppression with azathioprine and prednisone in recent-onset insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. New Engl J Med 1988;319:599–604.


9. Ludvigsson J, Heding L, Lieden G, Marner B, Lernmark A. Plasmapheresis in the initial treatment of insulindependent diabetes mellitus in children. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983;286:176–8.



10. Steffes MW, Sibley S, Jackson M, Thomas W. β-cell function and the development of diabetes-related complications in the diabetes control and complications trial. Diabetes Care 2003;26:832–6.


11. Marino KR, Lundberg RL, Jasrotia A, Maranda LS, Thompson MJ, Barton BA, et al. A predictive model for lack of partial clinical remission in new-onset pediatric type 1 diabetes. PLoS One 2017;12:e0176860.



12. Nwosu BU, Zhang B, Ayyoub SS, Choi S, Villalobos-Ortiz TR, Alonso LC, et al. Children with type 1 diabetes who experienced a honeymoon phase had significantly lower LDL cholesterol 5 years after diagnosis. PLoS One 2018;13:e0196912.



13. Niedzwiecki P, Pilacinski S, Uruska A, Adamska A, Naskret D, Zozulinska-Ziolkiewicz D. Influence of remission and its duration on development of early microvascular complications in young adults with type 1 diabetes. J Diabetes Complications 2015;29:1105–11.


14. Fonolleda M, Murillo M, Vázquez F, Bel J, Vives-Pi M. Remission phase in paediatric type 1 diabetes: new understanding and emerging biomarkers. Horm Res Paediatr 2017;88:307–15.


15. Wolfsdorf JI, Glaser N, Agus M, Fritsch M, Hanas R, Rewers A, et al. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2018: Diabetic ketoacidosis and the hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state. Pediatr Diabetes 2018;19:155–77.


16. Esen İ, Demirel F, Tepe D, Kara Ö. Frequency of partial remission and related factors in children and adolescents diagnosed with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries 2015;35:230–5.

17. Neylon OM, White M, O’Connell MA, Cameron FJ. Insulin-dose-adjusted HbA1c-defined partial remission phase in a paediatric population-when is the honeymoon over? Diabet Med 2013;30:627–8.


18. Lundberg RL, Marino KR, Jasrotia A, Maranda LS, Barton BA, Alonso LC, et al. Partial clinical remission in type 1 diabetes: a comparison of the accuracy of total daily dose of insulin of <0.3 units/kg/day to the gold standard insulindose adjusted hemoglobin A1c of ≤9 for the detection of partial clinical remission. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 2017;30:823–30.


19. Pecheur A, Barrea T, Vandooren V, Beauloye V, Robert A, Lysy PA. Characteristics and determinants of partial remission in children with type 1 diabetes using the insulin-dose-adjusted A1C definition. J Diabetes Res 2014;2014:851378.



20. Nagl K, Hermann JM, Plamper M, Schröder C, Dost A, Kordonouri O, et al. Factors contributing to partial remission in type 1 diabetes: analysis based on the insulin dose-adjusted HbA1c in 3657 children and adolescents from Germany and Austria. Pediatr Diabetes 2017;18:428–34.


21. Nielens N, Pollé O, Robert A, Lysy PA. Integration of routine parameters of glycemic variability in a simple screening method for partial remission in children with type 1 diabetes. J Diabetes Res 2018;2018:5936360.



22. Mente A, Razak F, Blankenberg S, Vuksan V, Darlene Davis A, Miller R, et al. Ethnic variation in adiponectin and leptin levels and their association with adiposity and insulin resistance. Diabetic Care 2010;33:1629–34.

23. Ehtisham S, Crabtree N, Clark P, Shaw N, Barrett T. Ethnic differences in insulin resistance and body composition in United Kingdom adolescents. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005;90:3963–9.


24. Chase HP, MacKenzie TA, Burdick J, Fiallo-Scharer R, Walravens P, Klingensmith G, et al. Redefining the clinical remission period in children with type 1 diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes 2004;5:16–9.

25. Aly H, Gottlieb P. The honeymoon phase: intersection of metabolism and immunology. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 2009;16:286–92.


26. Gleason CE, Gonzalez M, Harmon JS, Paul Robertson R. Determinants of glucose toxicity and its reversibility in the pancreatic islet β-cell line, HIT-T15. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2000;279:E997–1002.


27. Dost A, Herbst A, Kintzel K, Haberland H, Roth CL, Gortner L, et al. Shorter remission period in young versus older children with diabetes mellitus type 1. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 2007;115:33–7.


28. von Herrath M, Sanda S, Herold K. Type 1 diabetes as a relapsing-remitting disease? Nat Rev Immunol 2007;7:988–94.


29. Turtinen M, Härkönen T, Parkkola A, Ilonen J, Knip M. Sex as a determinant of type 1 diabetes at diagnosis. Pediatr Diabetes 2018;19:1221–8.


30. Crinò A, Pediatrico O, Gesù B, Gross TM, Pozzilli P, Mesturino CA, et al. Is the process of β-cell destruction in type 1 diabetes at time of diagnosis more extensive in females than in males? Is the process of b-cell destruction in type 1 diabetes at time of diagnosis more extensive in females than in males? Eur J Endocrinol 2001;145:757–61.

31. Arslanian SA, Heil BV, Becker DJ, Drash AL. Sexual dimorphism in insulin sensitivity in adolescents with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1991;72:920–6.


32. Komulainen J, Åkerblom HK, Lounamaa R, Knip M. Prepubertal girls with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus have higher exogenous insulin requirement than boys. Eur J Pediatr 1998;157:708–11.


33. Bowden SA, Duck MM, Hoffman RP. Young children (<5 yr) and adolescents (>12 yr) with type 1 diabetes mellitus have low rate of partial remission: diabetic ketoacidosis is an important risk factor. Pediatr Diabetes 2008;9(3 Pt 1):197–201.


34. Szypowska A, Skórka A. The risk factors of ketoacidosis in children with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes mellitus. Pediatr Diabetes 2011;12(4 Pt 1):302–6.


35. VanBuecken DE, Greenbaum CJ. Residual C-peptide in type 1 diabetes: what do we really know? Pediatr Diabetes 2014;15:84–90.


- TOOLS
- Related articles in APEM







