 |
 |
- Search
| Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab > Volume 26(4); 2021 > Article |
|
Abstract
Purpose
Sphingosine kinase is a lipid kinase that phosphorylates sphingosine to generate sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P). S1P regulates pancreatic islet β-cell endoplasmic reticulum stress and proliferation. Type 1 and type 2 diabetes share some key pathogenic processes. In this study, we investigated whether secretion of insulin and production of S1P is altered in alloxan and glucose-treated cells from the rat pancreatic β-cell line RIN-5F.
Methods
RIN-5F cells were treated with 2 mM alloxan and 20 mM glucose for 6 hours or 24 hours before being evaluated by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and Western blotting.
Results
Insulin secretion and expression was higher in RIN-5F cells treated with glucose compared to control cells. In contrast, alloxan treatment did not affect insulin secretion and expression in RIN-5F cells. Interestingly, compared with normal control levels, S1P/EDG-5 was increased in both alloxan and glucose-treated pancreatic β cell than normal control. Mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MAPK/ERK) inhibition strongly decreased the expression of insulin and S1P in glucose- or alloxan-treated RIN-5F cells.
Conclusions
We observe that production of S1P is increased in both diabetic cell models. In addition, MAPK/ERK signaling regulates secretion of insulin and S1P expression in pancreatic β-cells. Based on the literature and our findings, S1P may be a promising agent for the treatment of insulin-related disorders.
∙ Sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) contributes to the destruction of pancreatic β-cell.
∙ S1P production and insulin secretion are regulated through MAPK/ERK in diabetes in vitro.
∙ S1P may be a new therapeutic target in diabetes.
There are a number of causes of diabetes mellitus, resulting from dysfunction of β-cell insulin production and/or insulin resistance in peripheral organs [1,2]. Type 1 diabetes is caused by an autoimmune assault on pancreatic β-cells, resulting in decreased insulin production. In contrast, type 2 diabetes is caused by insulin resistance. Obesity and related inflammation are known as risk factors for type 2 diabetes. Although type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes have different pathogenesis, secondary comorbidities such as hypertension, hyperlipidemia, nephropathy, and retinopathy can develop in patients of either type of diabetes when not controlled [3,4]. Furthermore, exposure to excess lipids can cause a gradual decrease in pancreatic β-cell mass and decreased pancreatic β-cell functions such as insulin production in uncontrolled type 2 diabetes [5]. Therefore, both type 1 and type 2 diabetes share some similar phenotypes and comorbidities.
As a potent sphingolipid mediator, sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) is a crucial signaling molecule that modulates a variety of cellular functions [6,7]. S1P binds to S1P receptors 1–5 (transmembrane G protein-coupled receptors) to activate various intracellular and extracellular signal transduction mechanisms such as apoptosis, cell migration, differentiation, and inflammation [8,9]. Elevated S1P plasma levels are known to play an important role in metabolic syndrome, and elevated S1P levels are observed in type 2 diabetic patients [7,10]. In streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes animal models, S1P contributes to the progression of pancreatic β-cell destruction through S1P receptor-2 (S1P2) [11]. Likewise, S1P2 is known as endothelial differentiation, G protein-coupled receptor 5 (EDG5) and EDG5 signaling is known to be associated with insulin and pancreatic β-cells. However, the molecular mechanisms of S1P have not been fully elucidated in type 1 and type 2 diabetes. We examined the level of S1P in type 1 and type 2 experimental models of diabetes, and also tested relation between insulin signaling and S1P.
The rat pancreatic β-cell line RIN-5F was obtained from the European Collection of Animal Cell Cultures (America Type Culture Collection, CRL-11605; ATCC, VA, USA). Cells were cultured in Roswell Park Memorial Institute medium (cat. A1049101, Gibco, Gaithersburg, MD, USA) containing L-glutamine (Gibco) and supplemented with fetal bovine serum (Gibco) and an antibiotic-antimycotic mixture (Gibco). Cell cultures were maintained at 37℃ in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2.
Sources of reagents were as follows: glucose and alloxan (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA); a specific inhibitor for extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), PD98059 (Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA, USA); anti-S1P/EDG5, anti-pSPHK2, anti-SPHK2, anti-insulin, and anti-SREBP antibodies (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA); anti-pERK1/2, anti-ERK1/2, anti-pAKT, anti-AKT, anti-β-actin, and horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies (Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA, USA). Western blots were detected using an enhanced chemiluminescence reagent (Amersham Bioscience, Amersham, UK).
Morphological changes in cells were observed under an inverted phase-contrast microscope (Leica, Wetzlar, Germany). The effects of alloxan and glucose on pancreatic β-cells were observed for 24 hours. Photographs were taken at 200×magnification using a digital camera.
Cells were plated in 96-well culture plates at 1×106 cells/mL in culture medium and allowed to attach for 24 hours. The medium was then discarded and replaced with fresh medium containing various concentrations of glucose or alloxan. After 24-hour incubation, 10 μL of the Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8, Abcam, Cambridge, MA, USA) reagent was added and culturing was continued for 1 hour in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2. Absorbances at 450 nm were measured by a microplate reader (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA).
The cell culture medium was harvested and insulin present in the supernatant was measured using human insulin enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (Sigma-Aldrich) and S1P (MyBioSource, San Diego, CA, USA) kits according to the manufacturers' instructions.
Protein concentration was determined using a Bio-Rad Bradford kit (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA). Samples were boiled for 5 minutes and equal volumes were separated through sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Luminescent signals were analyzed using an ImageQuant LAS 4000 Scanner (GE Healthcare, Piscataway, NJ, USA).
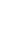
Before making alloxan-induced type 1 and glucose-induced type 2 cell models, we first examined their effect on the viability of RIN-5F cells. Cells were treated with glucose or alloxan for 24 hours and viability was measured using the CCK-8 assay. As shown in Fig. 1A, treatment of RIN-5F cells with 2 mM alloxan and 20 mM glucose reduced cell viability by 20% (Fig. 1A, B). These results were confirmed by phase-contrast microscopy. As shown in Fig. 1C, control RIN-5F cells maintained in medium alone exhibited a rounded cobblestone appearance. When exposed to 2 mM alloxan and 20 mM glucose for 24 hours, RIN-5F cells detached from the dish showing cell rounding, cytoplasmic blebbing, and an irregular shape. These results are consistent with the known effects of glucose and alloxan in the diabetic cell model.
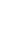
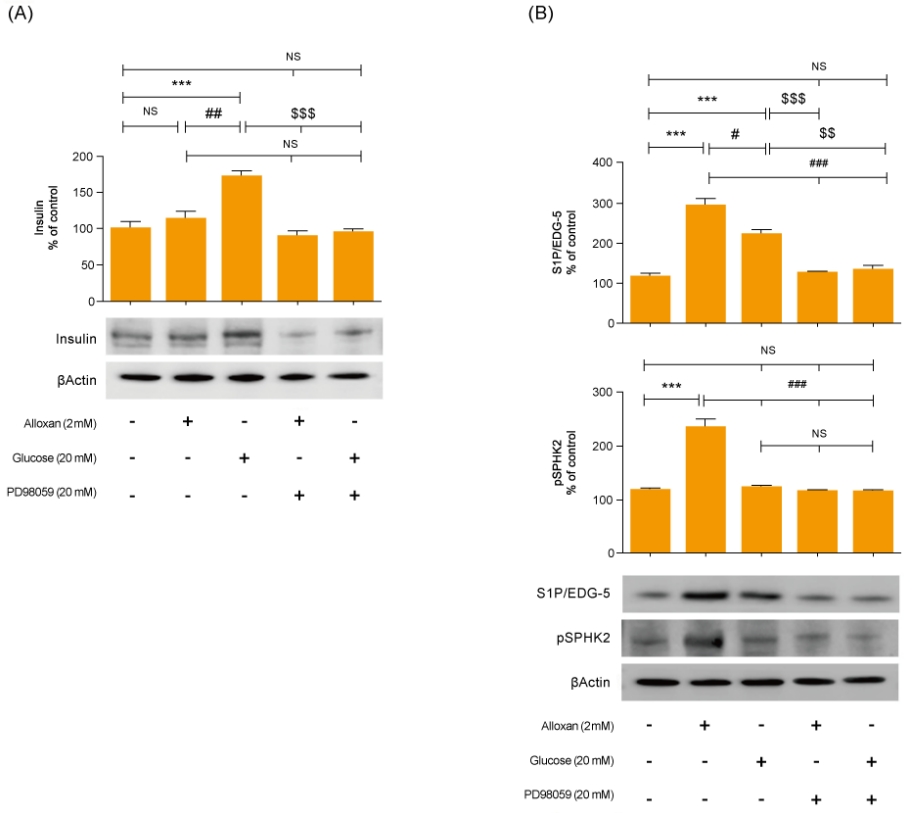
As shown in Fig. 2A and B, there was no change in insulin secretion in RIN-5F cells treated with 2 mM alloxan. In contrast, insulin secretion was increased in RIN-5F cells treated with 20 mM glucose compared to control cells.
We conducted immunoblotting and confirmed strongly increased insulin expression in RIN-5F cells treated with 20 mM glucose (Fig. 2A). In addition, the expression of S1P/EDG-5 was increased in both alloxan and glucose-treated beta cells relative to the control. Interestingly, pSPHK2 was specifically increased in 2 mM alloxan-treated RIN-5F cells compared to the control cells and 20 mM glucose-treated cells (Fig. 2B).
Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and AKT play key roles in glucose metabolism. To identify the precise MAPK/ERK signaling pathway involved in the relationship between S1P and insulin in alloxan and glucose-treated RIN-5F cells, we utilized a specific inhibitor for ERK (PD98059). Fig. 3 shows that it strongly induced MAPK/ERK and reduced AKT phosphorylation in both alloxan- and glucose-treated RIN-5F cells. Interestingly, phosphorylation of MAPK/ERK was increased more strongly in alloxan- than in glucose-treated RIN-5F cells. By treating RIN-5F cells with PD98059, we confirmed that the upregulation of insulin, S1P/EDG-5 and pSPHK2 were MAPK/ERK-dependent. Specifically, PD98059 strongly inhibited the expression of insulin, S1P/EDG-5 and pSPHK2 in glucose- or alloxan-treated RIN-5F cells (Fig. 4A, B).
Regulation of pancreatic β-cell mass affects a variety of physiological and pathological processes, such as apoptosis, autoimmunity, glucotoxicity, and insulin resistance, and is important for insulin secretion and glucose homeostasis [12]. S1P is a unique bioactive lipid mediator that is generated from sphingomyelin metabolites and plays an important role in DNA synthesis, Ca2+ mobilization, MAPK pathway activation [13,14], and the proliferation and survival functions of islet β-cells [15].
S1P is known to regulate insulin synthesis and resistance, reduce blood glucose levels, maintain blood vessels, and decrease inflammation [16]. However, the pharmacological roles of S1P in glucose metabolism remain unclear, particularly in terms of islet cell functions.
We used alloxan-induced type 1, and glucose-induced type 2 diabetes cell models [17-20]. Alloxan increases DNA fragmentation and inhibits glucose-stimulated insulin secretion, resulting in cell death [21]. In this study, we discovered that expression of S1P/EDG-5 was increased both in type 1 and in type 2 cell models relative to the normal control, and its level was also slightly higher in the type 1 cell model compared to the type 2 cell model (Fig. 2). Interestingly, pSPHK2 expression was not increased in glucose-induced type 2 diabetes cell models, which was like control. Recently, S1P is known to be involved in insulin secretion not only in pSPHK2 signal pathway, but also by regulating focal attachment kinase (FAK)/Src and Rho-related protein kinase (ROCK). Our results suggest that the expression of S1P in the type 2 cell model is related to FAK/Src and ROCK pathway.
AKT and ERK play important roles in regulating apoptosis of pancreatic β cells [22]. In addition, the ERK pathway is involved in regulating glucose-induced insulin secretion in a β-cell line [23]. Our data showed that both alloxan- and glucose-treated β-cells exhibited significantly increased ERK phosphorylation and reduced AKT phosphorylation compared to the control. Furthermore, an ERK inhibitor significantly attenuated the increased S1P/EDG5 expression and insulin secretion in the alloxan- and glucose-treated β-cells. This suggests that S1P has an important role in insulin secretion associated with MAPK/ERK signaling pathway in both type 1 and type 2 cell models. Our study was limited by the fact it uses an in vitro β-cell model. However, this experimental beta cell model is a kind of pilot study for future nonobese diabetic mice study; other beta cell model had been reported. Numerous studies have investigated S1P and its role in diabetes and various other diseases [24,25]. One study using human β cells reported that sphingolipid modulation represents a promising therapeutic route in type 1 diabetes [26].
In conclusion, we have identified that the expression of S1P/EGF was increased in diabetes models compared to the control, moreover, the finding this study also lead us to conclude that ERK signaling is regulated through the relationship between S1P and insulin in both type 1 and type 2 cell models. These results suggest that S1P should be considered a new treatment target for apoptosis, insulin resistance, and diabetic complications in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was presented at the 69th Conference of the Korean Pediatric Society in 2019.
Fig. 1.
Effects of different concentrations of glucose and alloxan on viability of RIN-5F cells. (A, B) CCK reduction was calculated to measure cellular proliferation. RIN-5F cells were treated with alloxan ranging from 0.5 to 4 mM and glucose ranging from 5 to 30 mM. (C) Phase-contrast photograph of change in cellular morphology of RIN-5F cells. Magnifications ×40. The data are representative of 3 independent experiments and quantified as mean±standard error of the mean (n=3–5). Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn post hoc test, ***P<0.001 compared to normal control. CCK, Cell Count Kit; NC, normal control.
Fig. 2.
Effects of insulin and S1P production on glucose and alloxan-treated RIN-5F cells. RIN-5F cells were treated with 2 mM alloxan and 20 mM glucose for 24 hours. (A) The protein extract was determined using by Western blot. β-actin was used to confirm equal sample loading control. (B) Western blotting was quantified by densitometric analysis. The data are representative of 3 independent experiments and quantified as mean±standard error of the mean (n=3–5). Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn post hoc test, *P<0.05, ***P<0.001 versus normal control; ###P<0.001 versus alloxan treatment group. S1P/EDG-5, sphingosine 1-phosphate/endothelial differentiation, G protein-coupled receptor 5; pSPHK2, phospho-sphingosine kinase 2; tSPHK2, total-sphingosine kinase 2; NS, not significant.
Fig. 3.
Alloxan and glucose-induced insulin signaling in RIN-5F cells. Phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase (pERK) (A) and phosphorylated AKT (pAKT) (B) were measured in RIN-5F cells treated with alloxan and glucose for 6 hours. β-actin was used to confirm equal sample loading control. Western blotting was quantified by densitometric analysis. The data are representative of 3 independent experiments and quantified as mean±standard error of the mean (n=3–5). Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn post hoc test, *P<0.05, ***P<0.001 versus normal control cells; ###P<0.001 versus alloxan treatment group. NS, not significant.

Fig. 4.
Inhibition of MAPK/ERK regulates alloxan and glucose-induced insulin, S1P/EDG-5 and pSPHK2 expression. RIN-5F cells were pretreated with ERK inhibitor (PD98059) for 30 min and then stimulated with alloxan and glucose for 24 hours. β-actin was used to confirm equal sample loading control. Western blotting was quantified by densitometric analysis. The data are representative of 3 independent experiments and quantified as mean±standard error of the mean (n=3–5). Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn post hoc test, ***P<0.001 versus normal control cells; #P<0.05, ###P<0.001 versus alloxan treatment group, $$P<0.01, $$$P<0.001 versus glucose treatment group. MAPK/ERK, mitogenactivated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase; S1P/EDG-5, sphingosine 1-phosphate/endothelial differentiation; G protein-coupled receptor 5, pSPHK2: phospho-sphingosine kinase2; NS, not significant.
References
1. Craig ME, Jefferies C, Dabelea D, Balde N, Seth A, Donaghue KC, et al. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2014. Definition, epidemiology, and classification of diabetes in children and adolescents. Pediatr Diabetes 2014;15 Suppl 20:4–17.
3. Pinhas-Hamiel O, Zeitler P. Acute and chronic complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents. Lancet 2007;369:1823–31.


4. Craig ME, Jones TW, Silink M, Ping YJ. Diabetes care, glycemic control, and complications in children with type 1 diabetes from Asia and the Western Pacific Region. J Diabetes Complications 2007;21:280–7.


5. Saini V. Molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus. World J Diabetes 2010;1:68–75.



6. Arish M, Alaidarous M, Ali R, Akhter Y, Rub A. Implication of sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling in diseases: molecular mechanism and therapeutic strategies. J Recept Signal Transduct Res 2017;37:437–46.


7. Chen W, Lu H, Yang J, Xiang H, Peng H. Sphingosine 1-phosphate in metabolic syndrome (review). Int J Mol Med 2016;38:1030–8.


8. Rosen H, Stevens RC, Hanson M, Roberts E, Oldstone MB. Sphingosine-1-phosphate and its receptors: structure, signaling, and influence. Annu Rev Biochem 2013;82:637–62.


9. Ng ML, Wadham C, Sukocheva OA. The role of sphingolipid signalling in diabetes associated pathologies (review). Int J Mol Med 2017;39:243–52.



10. R andri amb o avonjy V, B aden ho op K, S chmidt H, Geisslinger G, Fisslthaler B, Fleming I. The S1P(2) receptor expressed in human platelets is linked to the RhoA-Rho kinase pathway and is down regulated in type 2 diabetes. Basic Res Cardiol 2009;104:333–40.


11. Imasawa T, Koike K, Ishii I, Chun J, Yatomi Y. Blockade of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 2 signaling attenuates streptozotocin-induced apoptosis of pancreatic beta-cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2010;392:207–11.


12. Alshatwi AA, Subash-Babu P. Aloe-emodin protects RIN-5F (pancreatic β-cell) cell from glucotoxicity via regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokine and downregulation of bax and caspase 3. Biomol Ther (Seoul) 2016;24:49–56.



13. Spiegel S, Milstien S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate: signaling inside and out. FEBS Lett 2000;476:55–7.


14. He Y, Shi B, Zhao X, Sui J. Sphingosine-1-phosphate induces islet β-cell proliferation and decreases cell apoptosis in high-fat diet/streptozotocin diabetic mice. Exp Ther Med 2019;18:3415–24.



15. Hatoum D, Haddadi N, Lin Y, Nassif NT, McGowan EM. Mammalian sphingosine kinase (SphK) isoenzymes and isoform expression: challenges for SphK as an oncotarget. Oncotarget 2017;8:36898–929.



16. Haass NK, Nassif N, McGowan EM. Switching the sphingolipid rheostat in the treatment of diabetes and cancer comorbidity from a problem to an advantage. Biomed Res Int 2015;2015:165105.



17. Ighodaro OM, Adeosun AM, Akinloye OA. Alloxan-induced diabetes, a common model for evaluating the glycemic-control potential of therapeutic compounds and plants extracts in experimental studies. Medicina (Kaunas) 2017;53:365–74.


18. Wysham C, Shubrook J. Beta-cell failure in type 2 diabetes: mechanisms, markers, and clinical implications. Postgrad Med 2020;132:676–86.


19. Poitout V, Robertson RP. Minireview: secondary beta-cell failure in type 2 diabetes--a convergence of glucotoxicity and lipotoxicity. Endocrinology 2002;143:339–42.


20. Tsubouchi H, Inoguchi T, Sonta T, Sato N, Sekiguchi N, Kobayashi K, et al. Statin attenuates high glucose-induced and diabetes-induced oxidative stress in vitro and in vivo evaluated by electron spin resonance measurement. Free Radic Biol Med 2005;39:444–52.


21. Rho HW, Lee JN, Kim HR, Park BH, Park JW. Protective mechanism of glucose against alloxan-induced beta-cell damage: pivotal role of ATP. Exp Mol Med 2000;32:12–7.


22. Lei H, Han J, Wang Q, Guo S, Sun H, Zhang X. Effects of sesamin on streptozotocin (STZ)-induced NIT-1 pancreatic β-cell damage. Int J Mol Sci 2012;13:16961–70.



23. Longuet C, Broca C, Costes S, Hani EH, Bataille D, Dalle S. Extracellularly regulated kinases 1/2 (p44/42 mitogen-activated protein kinases) phosphorylate synapsin I and regulate insulin secretion in the MIN6 beta-cell line and islets of Langerhans. Endocrinology 2005;146:643–54.


24. Holland WL, Summers SA. Sphingolipids, insulin resistance, and metabolic disease: new insights from in vivo manipulation of sphingolipid metabolism. Endocr Rev 2008;29:381–402.



- TOOLS
- Related articles in APEM







