 |
 |
- Search
| Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab > Volume 21(3); 2016 > Article |
|
Abstract
Vitamin D hydroxylation-deficient rickets type 1A (VDDR1A) is an autosomal recessively-inherited disorder caused by mutations in CYP27B1 encoding the 1α-hydroxylase enzyme. We report on a female patient with VDDR1A who presented with hypocalcemic seizure at the age of 13 months. The typical clinical and biochemical features of VDDR1A were found, such as hypocalcemia, increased alkaline phosphatase, secondary hyperparathyroidism and normal 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (25(OH)D3). Radiographic images of the wrist showed metaphyseal widening with cupping and fraying of the ulna and distal radius, suggesting rickets. A mutation analysis of the CYP27B1 gene identified a homozygous mutation of c.589+1G>A in the splice donor site in intron 3, which was known to be pathogenic. Since that time, the patient has been under calcitriol and calcium treatment, with normal growth and development. During the follow-up period, she did not develop genu valgum, scoliosis, or nephrocalcinosis.
Vitamin D hydroxylation-deficient rickets type 1A (VDDR1A) (MIM 264700), or pseudo-vitamin D-deficiency rickets type 1, is an autosomal recessively inherited disorder resulting from deficiency of renal 1α-hydroxylase1) and characterized by hypotonia, growth retardation, muscle weakness, severe rickets, hypocalcemia, and secondary hyperparathyroidism2,3,4). VDDR1A is an extremely rare disease and the incidence in Denmark is estimated at 0.3/100,000 individuals per year5). To date, 5 patients with VDDR1A have been reported in Korea6,7). However, it is assumed that there are many unreported or genetically unconfirmed cases. The biochemical hallmark of VDDR1A is normal 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (25(OH)D3) with low 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1,25(OH)2D3) levels8). Other laboratory findings are characterized by hypocalcemia, hypophosphatemia, and increased serum concentrations of parathyroid hormone (PTH)9).
The CYP27B1 gene encodes P450c1α, renal and keratinocyte 1α-hydroxylase, and consists of 9 exons spanning 5 kb10,11,12). To date, 68 different mutations have been reported worldwide (http://www.hgmd.org). Several mutations in the CYP27B1 gene are more frequently reported in certain ethnic groups2,6,8). The disease is more frequent in the French Canadian population of the Saguenay region of Quebec8).
Treatment with active vitamin D (1,25(OH)2D3 or calcitriol) improves the clinical and biochemical abnormalities13). We report on a female with VDDR1A, who presented with hypocalcemic seizure at the age of 13 months. We describe the clinical features, molecular characteristics, and clinical course of the patient, with a review of the literatures.
A 13-month-old female was admitted to the Pediatric Emergency Department due to a generalized tonic-clonic seizure lasting for a few minutes. She was born in the 39th week of gestation without perinatal problems. She could control her head 4 months after birth and rolled over at 5 months. At 7 months, she could sit alone. However, she could not stand or walk until 14 months of age.
Biochemical findings showed a low serum calcium of 4.8 mg/dL (normal range, 8.3–10 mg/dL); phosphorus of 4.3 mg/dL (normal range, 2.5–4.5 mg/dL), and elevated alkaline phosphatase of 1,665 U/L (normal range, <269 U/L). PTH was 178 pg/mL (normal range, 10–65 pg/mL) and 25(OH) D3 was 75.1 ng/mL. Initial 1,25(OH)2D3 level was 5.26 pg/mL (normal range, 15–90 pg/mL). Echocardiography showed QT prolongation. An evaluation for renal tubular acidosis was normal, with normal urine pH. Tubular reabsorption of phosphate was 88%. Radiographic images of the wrist showed cupping and fraying of the ulna and distal radius, as well as metaphyseal widening, indicating rickets (Fig. 1A). Harrison sulcus and rachitic rosary were also observed (Fig. 1B). There was no family history of rickets.
A mutation analysis of the CYP27B1 gene was performed at the age of 10 years. All coding exons and intron in flanking regions of CYP27B1 were amplified by polymerase chain reaction and directly sequenced using an ABI3130x1 Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). She was homozygous for c.589+1G>A in the splice donor site in intron 3 (Fig. 2), which was reported to be pathogenic14).
The patient was immediately treated with intravenous calcium gluconate (20 mg/kg/day) for the hypocalcemic seizure. After her symptoms were relieved, she was discharged with oral calcium carbonate (30 mg/kg/day of elemental calcium) and calcitriol (0.5 µg/day). Compliance with the treatment was good, resulting in rapid amelioration of the clinical, biochemical, and radiological abnormalities. The serum calcium normalized within a month, and there were no recurrent seizures. The cupping and fraying of the ulna and distal radius was improved after 5 months of therapy. After 2 years of treatment with calcitriol and calcium supplement, follow-up radiological images demonstrated fully healing of the long-bone bowing and flaring (Fig. 1C). The patient's biochemical parameters and anthropometry during the follow-up period are shown in Table 1.
The patient had neither genu valgum/varum nor scoliosis. Nephrocalcinosis did not develop during the follow-up period. But she had severe dental caries. At her last visit at the age of 17.8 years, her height and weight were 166 cm (1.1 standard deviation score [SDS]) and 68 kg (1.6 SDS), respectively, and she had no symptoms with the calcitriol (0.5 µg/day) and calcium (400 mg/day of elemental calcium) treatment (Fig. 3)
This report described long-term clinical course of a patient with VDDR1A, who was confirmed by molecular analysis of the CYP27B1 gene analysis. A few VDDR1A cases with short-term clinical courses have been reported in Korea6,7).
The biologically inactive prohormones, such as vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) are sequentially hydroxylated in the liver and kidneys by hepatic 25-hydroxylase (CYP2R1) and renal 1α-hydroxylase (CYP27B1), respectively15,16). The active form of vitamin D (1,25(OH)2D3) plays an important role in calcium homeostasis and bone growth16,17,18). Renal synthesis of 1,25(OH)2D3 from 25OHD3 by 1α-hydroxylation is the rate-limiting step in the synthesis of active form of vitamin D16,17,18). 1α-hydroxylation is stimulated by PTH and negatively regulated by fibroblast growth factor-23 and 1,25(OH)2D3 itself6).
The biochemical findings in VDDR1A are characterized by hypocalcemia, hypophosphatemia, and low or undetectable serum levels of 1,25(OH)2D3 despite high serum levels of PTH and 25(OH)D3
9). The clinical symptoms and signs are similar to hypophosphatemic rickets. However, it is possible to differentiate VDDR1A from hypophosphatemic rickets by low serum concentrations of 1,25(OH)2D3 and high PTH. Increased PTH and renal excretion of phosphate results in hypophosphatemia9) because PTH reduces phosphate and increases calcium reabsorption from the renal proximal tubules, and also increases serum calcium via osteoclast-mediated bone resorption19). These mechanisms result in severely elevated serum alkaline phosphatase19).
In the present study, the c.589+1G>A mutation was identified, which was reported to cause premature stop codon at 63 bp downstream from the end of exon 314). G-to-A substitution in the first nucleotide of a splice site is a frequent mutation in numerous genes, resulting in skipping of the exon20). Deletions, premature terminations due to splice site mutations, and insertions are common defects that disrupt or eliminate the heme-binding domain of CYP27B1 and thereby inactivate this enzyme6).
Calcitriol treatment (10–400 ng/kg/day) results in regression of the symptoms and normalization of laboratory findings, including decreased calcium and phosphorus, and increased alkaline phosphatase and PTH2). At her most recent visit, the biochemical values were improved to serum calcium of 8.5 mg/dL; phosphorus 3.1 mg/dL, and decreased alkaline phosphatase 90 U/L; PTH was 104 pg/mL. If there are persistently elevated PTH levels after initiation of treatment with calcium supplementation, secondary hyperparathyroidism should be ruled out. Most patients show significant height gains with calcitriol, similar to our case. In cases of growth failure during this treatment, poor adherence to the medication should be considered2). In conclusion, we report a case of VDDR1A presenting in a patient with hypocalcemic seizure and rickets, in whom a homozygous splicing mutation (c.589+1G>A) was identified.
References
1. Fu GK, Lin D, Zhang MY, Bikle DD, Shackleton CH, Miller WL, et al. Cloning of human 25-hydroxyvitamin D-1 alpha-hydroxylase and mutations causing vitamin D-dependent rickets type 1. Mol Endocrinol 1997;11:1961–1970. PMID: 9415400.

2. Demir K, Kattan WE, Zou M, Durmaz E, BinEssa H, Nalbantoğlu Ö, et al. Novel CYP27B1 Gene Mutations in Patients with Vitamin D-Dependent Rickets Type 1A. PLoS One 2015;10:e0131376. PMID: 26132292.



3. Fraser D, Kooh SW, Kind HP, Holick MF, Tanaka Y, DeLuca HF. Pathogenesis of hereditary vitamin-D-dependent rickets. An inborn error of vitamin D metabolism involving defective conversion of 25-hydroxyvitamin D to 1 alpha, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D. N Engl J Med 1973;289:817–822. PMID: 4357855.


4. Babiker AM, Al Gadi I, Al-Jurayyan NA, Al Nemri AM, Al Haboob AA, Al Boukai AA, et al. A novel pathogenic mutation of the CYP27B1 gene in a patient with vitamin D-dependent rickets type 1: a case report. BMC Res Notes 2014;7:783. PMID: 25371233.



5. Beck-Nielsen SS, Brock-Jacobsen B, Gram J, Brixen K, Jensen TK. Incidence and prevalence of nutritional and hereditary rickets in southern Denmark. Eur J Endocrinol 2009;160:491–497. PMID: 19095780.


6. Kim CJ, Kaplan LE, Perwad F, Huang N, Sharma A, Choi Y, et al. Vitamin D 1alpha-hydroxylase gene mutations in patients with 1alpha-hydroxylase deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007;92:3177–3182. PMID: 17488797.



8. Wang JT, Lin CJ, Burridge SM, Fu GK, Labuda M, Portale AA, et al. Genetics of vitamin D 1alpha-hydroxylase deficiency in 17 families. Am J Hum Genet 1998;63:1694–1702. PMID: 9837822.



9. Malloy PJ, Feldman D. Genetic disorders and defects in vitamin d action. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 2010;39:333–346. PMID: 20511055.



10. Fu GK, Portale AA, Miller WL. Complete structure of the human gene for the vitamin D 1alpha-hydroxylase, P450c1alpha. DNA Cell Biol 1997;16:1499–1507. PMID: 9428799.


11. Monkawa T, Yoshida T, Wakino S, Shinki T, Anazawa H, Deluca HF, et al. Molecular cloning of cDNA and genomic DNA for human 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 1 alpha-hydroxylase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1997;239:527–533. PMID: 9344864.


12. Kitanaka S, Takeyama K, Murayama A, Sato T, Okumura K, Nogami M, et al. Inactivating mutations in the 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 1alpha-hydroxylase gene in patients with pseudovitamin D-deficiency rickets. N Engl J Med 1998;338:653–661. PMID: 9486994.


13. Durmaz E, Zou M, Al-Rijjal RA, Bircan I, Akçurin S, Meyer B, et al. Clinical and genetic analysis of patients with vitamin D-dependent rickets type 1A. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2012;77:363–369. PMID: 22443290.


14. Kitanaka S, Murayama A, Sakaki T, Inouye K, Seino Y, Fukumoto S, et al. No enzyme activity of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 1alpha-hydroxylase gene product in pseudovitamin D deficiency rickets, including that with mild clinical manifestation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999;84:4111–4117. PMID: 10566658.

15. Miller WL, Portale AA. Vitamin D 1 alpha-hydroxylase. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2000;11:315–319. PMID: 10996526.


16. Kitanaka S, Takeyama K, Murayama A, Kato S. The molecular basis of vitamin D-dependent rickets type I. Endocr J 2001;48:427–432. PMID: 11603564.


17. Kato S, Yoshizazawa T, Kitanaka S, Murayama A, Takeyama K. Molecular genetics of vitamin D-dependent hereditary rickets. Horm Res 2002;57:73–78. PMID: 12006701.


18. Glorieux FH, Pettifor JM. Vitamin D/dietary calcium deficiency rickets and pseudo-vitamin D deficiency rickets. Bonekey Rep 2014;3:524. PMID: 24818008.



19. Akerström G, Hellman P, Hessman O, Segersten U, Westin G. Parathyroid glands in calcium regulation and human disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2005;1040:53–58. PMID: 15891005.


20. Cooper DN, Krawczak M, Antonaratis SE. The nature and mechanism of human gene mutation. Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle Det al., editors. The metabolic and molecular bases of inherited disease. 7th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill. 1995;pp 259–291.
Fig. 1
Radiographic images of the patient with vitamin D hydroxylation-deficient rickets type 1A. (A) Simple X-ray findings show fraying and cupping of the radius, ulnar, tibia and fibula, and metaphyseal widening at presentation. (B) Harrison sulcus and rachitic rosary were also observed (arrow). (C) After 2 years of treatment, marked improvement in widening and flaring of metaphysis of long bone were revealed.
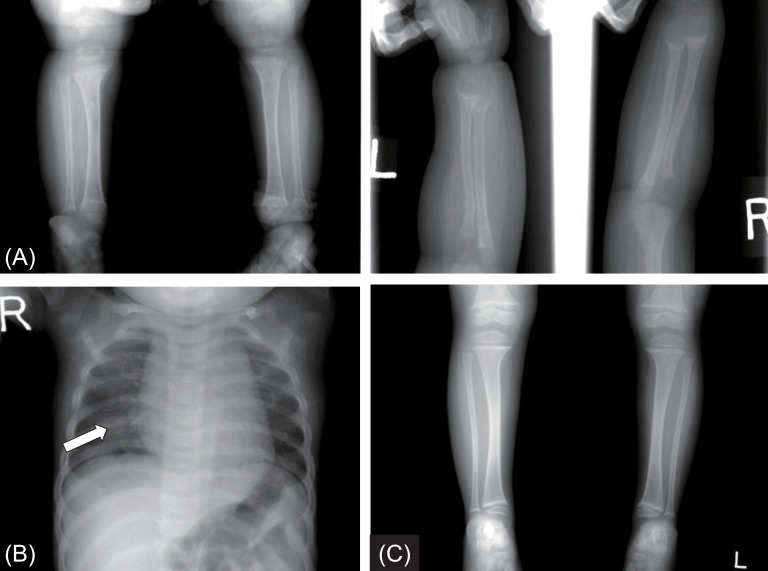
Fig. 2
Mutation analysis of the CYP27B1 gene. Partial sequences of CYP21B1 show homozyous splicing mutation in intron 3 (c.589+1G>A).

Fig. 3
Growth curve of of the patient with vitamin D hydroxylation-deficient rickets type 1A. Mid parental height (arrow).
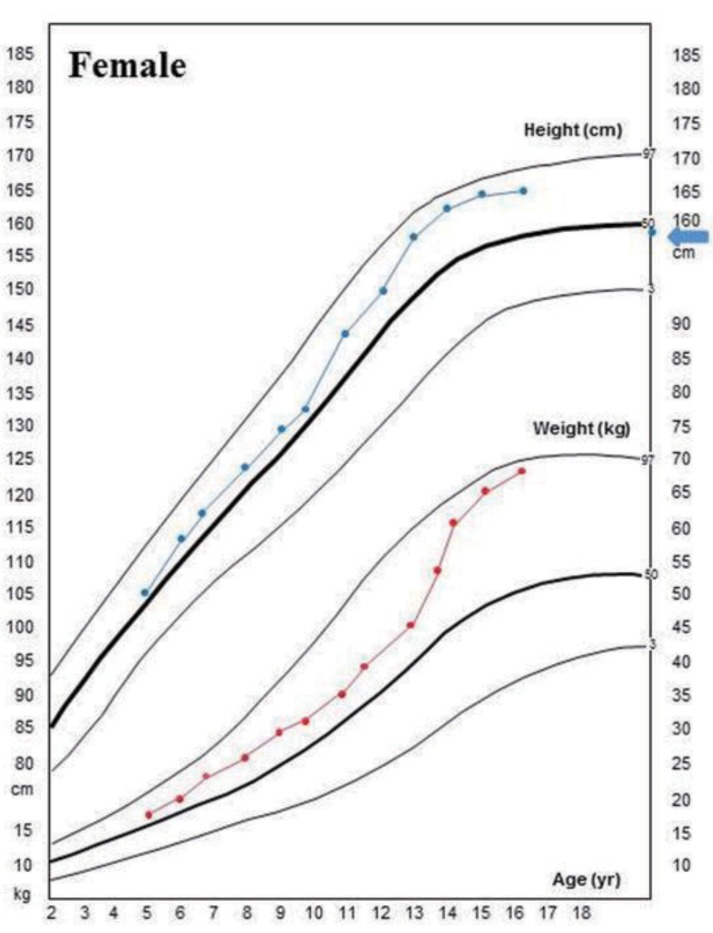
Table 1
Clinical and laboratory findings of the patient with vitamin D hydroxylation-deficient rickets type 1A
- TOOLS
- Related articles in APEM






