 |
 |
- Search
| Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab > Volume 21(1); 2016 > Article |
|
Abstract
Purpose
Williams-Beuren syndrome (WBS) is caused by a hemizygous microdeletion of chromosome 7q11.23 and is characterized by global cognitive impairment, dysmorphic facial features, and supravalvular aortic stenosis. Endocrine dysfunctions have been reported in patients with WBS. This study was performed to investigate the frequency, clinical features, and outcomes of endocrine dysfunctions in children with WBS.
Methods
One hundred two patients were included. The diagnosis was confirmed by chromosome analysis and fluorescent in situ hybridization. Medical charts were reviewed retrospectively to analyze endocrine dysfunctions such as short stature, precocious puberty, thyroid dysfunctions, and hypocalcemia.
Results
The age at diagnosis was 3.7±4.4 years (one month to 19 years). Height- and weight-standard deviation score (SDS) were –1.1±1.1 and –1.4±1.4 at presentation, respectively. Short stature was found in 26 patients (28.3%) among those older than 2 years. Body mass index-SDS increased as the patients grew older (P<0.001). Two males and one female (2.9%) were diagnosed with central precocious puberty. Nine patients (8.8%) were diagnosed with primary hypothyroidism at age 4.0±4.3 years (one month to 12.1 years); their serum thyroid stimulating hormone and free T4 levels were 15.2±5.4 µU/mL and 1.2±0.2 ng/dL, respectively. Hypercalcemia was observed in 12 out of 55 patients under age 3 (22%) at the age of 14.3±6.6 months (7 to 28 months) with a mean serum calcium level of 13.1±2.1 mg/dL.
Williams-Beuren syndrome (WBS) is a rare disease with an estimated incidence of 1 in 7,500-10,000 persons1,2) that is caused by a hemizygous microdeletion of chromosome 7q11.23. The chromosome 7q11.23 region contains 26 to 28 genes2,3), including the ELN, gene which is known to contribute to the phenotype4). Several other genes in the WBS critical region are known to be implicated in its phenotype5). The FZD9, BAZ1B, and STX1A genes in mouse models are known to cause osteopenia, hypercalcemia, and impaired glucose tolerance, respectively4). WBS is mostly diagnosed by fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) using an ELN specific probe that demonstrates deletion of ELN4,6). Other diagnostic methods include multiplex ligation dependent-probe amplification analysis, microsatellite marker analysis, and quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis4).
Common clinical features of this syndrome include dysmorphic facial features, global cognitive impairment, supravalvular aortic stenosis, and renal and urinary tract abnormalities3). Endocrine abnormalities such as short stature, precocious puberty, hypothyroidism, and hypercalcemia accompany this syndrome6,7,8). Short stature, early puberty, subclinical hypothyroidism, overt hypothyroidism and hypercalcemia have been reported in 30% to 40%, 50%, 2%, 15%, and 5% to 15% of patients, respectively4,6,9). The pathophysiology and outcomes of endocrine symptoms remain to be elucidated and treatment is focused on relieving symptoms and preventing complications. This study was performed to investigate the frequency, clinical characteristics, and outcomes of endocrine manifestations in patients with WBS.
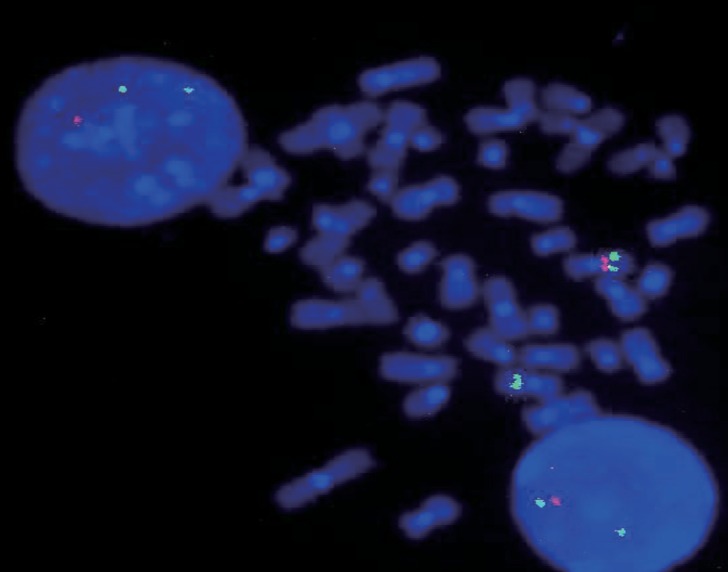
This study included 102 consecutive patients (64 males [62.7%] and 38 females [37.3%]) with WBS diagnosed between May 1993 and July 2015 in Asan Medical Center. The most common presenting sign was developmental delay (47.6%), followed by cardiac anomaly such as supravalvular aortic stenosis and mitral valve prolapse (31.1%), facial dysmorphism (5.8%), and failure to thrive (1.9%). FISH was performed in patients with clinical features of WBS such as typical facial dysmorphism, developmental delay, cardiac anomaly, and hypercalcemia. Deletion of the 7q11.23 region was identified by FISH in 102 patients (Fig. 1).
Auxological parameters such as height, weight, and body mass index (BMI) were analyzed retrospectively. Each parameter was expressed as a standard deviation score (SDS) according to the normative data from Korean reference sources10). Patients with short stature were defined as being of height below the third percentile and final adult height was reviewed among patients older than 18 years. Serum insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) levels were measured by immunoradiometric assay (Immunotech, Marseille, France) and expressed as z-scores calculated based on normative data from Korean reference sources11). Bone age was determined using the Greulich-Pyle method12).
Luteinizing hormone, follicle stimulating hormone, testosterone (males), or estradiol (females) levels were measured in patients with precocious puberty. Central precocious puberty was defined as the onset of breast development before the age of 8 years in girls and by the onset of testicular development (volume ≥4 mL) before the age of 9 years in boys13). Early puberty was defined as the onset of pubertal signs at 8–10 years in girls and 9–11 years in boys13). Central precocious puberty was diagnosed by a gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) stimulation test using an intravenous bolus of a standard dose of 2.5 µg/kg. Thyroid functions, including free T4 and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) levels, were measured in 62 patients. Patients with serum TSH levels higher than 10 µU/mL with normal or low T4 were considered to have hypothyroidism14,15). Patients whose TSH levels were slightly above 10 µU/mL were re-evaluated after 2–4 weeks later and those who had persistently high TSH levels were treated with levothyroxine. Serum calcium and phosphorus levels, nephrocalcinosis on kidney ultrasonography, and treatment methods with duration of treatment were assessed.
The age at diagnosis and last follow-up were 3.7±4.4 years (range, 1 month to 19 years) and 12±6.1 years (range, 25 months to 26 years), respectively. Height-SDS, weight-SDS, and BMISDS at presentation were –1.1±1.1, –1.4±1.4, and –1.4±1.3, respectively. Height-SDS, weight-SDS, and BMI-SDS at last follow-up were –1.0±1.1, –1.0±1.4, and –0.6±1.4, respectively. BMI-SDS increased as the patients grew older (P<0.001).
Short stature was found in 26 patients (28.3%) among those older than 2 years of age. Their height-SDS, weight-SDS, and BMI were –2.38±0.62 (range, –3.97 to –1.6 SDS), –1.74±1.53 (range, –3.95 to 1.8) and 18.2±4.6 kg/m2 (range, 13.1–34.5 kg/m2), respectively. Birth weight was 2.7±0.5 kg (range, 1.9–3.7 kg) in 15 patients whose birth weight data was available; 8 of them were small for gestational age. Five females and 1 male reached final adult height; the mean height of these females was 148.6±5.8 cm (–2.56±1.27 SDS) and that of 1 male was 167.8 cm (–0.97 SDS). Serum IGF-1 and IGFBP-3 levels were measured in 8 patients; IGF-1- and IGFBP-3-SDS were 0.82±1.82 (range, –1.39 to 4.03) and –0.37±1.56 (range, –1.53 to 3.05), respectively.
Two males and 1 female (3 of 102, 2.9%) were diagnosed with central precocious puberty and 2 males and 2 females displayed early puberty (4 of 102, 3.9%) but did not meet the criteria for central precocious puberty (Table 1). The 2 males with central precocious puberty were 8.8 years and 8.9 years old when they presented with testicular enlargement. The female patient with central precocious puberty presented with breast enlargement at the age of 7.4 years. The difference between bone age and chronological age (BA–CA) of the three patients with central precocious puberty was 1.8±0.5 years (range, 1.3–2.3 years). One of the male's predicted adult height (PAH) and midparental height were 159.1 cm and 168 cm, respectively. He was treated with a GnRH agonist for 28 months and grew from 135.7 cm (–0.21 SDS) at age 9.9 years to 145.6 cm (–0.64 SDS) at age 12.3 years, with a PAH of 162.7 cm. The other male patient was lost to follow-up. The female patient with a PAH of 153.1 cm and midparental height of 162 cm was administered a GnRH agonist for 3 years and grew from 127.6 cm (0.34 SDS) at age 8.1 years to 153 cm (–0.4 SDS) at the age of 11.1 years. Menarche occurred at the age of 12.1 years.
Nine patients (8.8%) were diagnosed with primary hypothyroidism at age 4.0±4.3 years (range, 1 month to 12.1 years); their serum TSH and free T4 levels were 15.2±5.4 µU/mL and 1.2±0.2 ng/dL, respectively (Table 2). Levothyroxine treatment was discontinued in 5 patients after normalization of thyroid hormone level and their treatment duration was 34±22.4 months (range, 9–70 months). Two patients with congenital hypothyroidism are still under treatment with levothyroxine at the current ages of 3 and 8 years. Two patients were not followed up. Thyroid autoantibody tests were negative in all patients. Thyroid ultrasonography was performed in 2 patients, and both of them showed thyroid hypoplasia.
The serum calcium level was measured before 3 years of age among 55 patients, with a serum calcium level of 10.6±1.7 mg/dL (range, 8.6–16.5 mg/dL). Hypercalcemia was observed in 12 patients (12 of 55, 22%) at the age of 14.3±6.6 months (range, 7–28 months), with a serum calcium level of 13.1±2.1 mg/dL (range, 11–16.5 mg/dL) (Table 3). Half of them required treatment to reduce their serum calcium level; intravenous hydration and diuretics were administered to 6 patients and all but 1 patient improved within several days to weeks. The other 6 patients showed spontaneous resolution of hypercalcemia. Parathyroid hormone levels were suppressed in all but 1 patient. Renal ultrasonography was performed in five patients and all of them displayed nephrocalcinosis.
This study demonstrated that endocrine dysfunctions such as short stature, precocious puberty, hypothyroidism, and hypercalcemia are relatively common in patients with WBS. Short stature and central precocious puberty were found in 28.3% and 2.9% of children, respectively. Thyroid dysfunction was diagnosed in 8.8% and it was managed with levothyroxine. Hypercalcemia was found in 22% of patients under the age of 3 years.
Short stature is not evident at birth, but it manifests in early childhood16,17). Short stature was reported in 33% at preschool age and 67% at school age in a previous Korean study18). However, about 50% to 60% of patients with WBS reach a final adult height below their target height range8,19). Short stature is caused by several factors, such as feeding difficulty, gastroesophageal reflux disease, vomiting, colic, and early puberty4). Feeding difficulties are reported in 70% to 80% of patients6). The gastrointestinal symptoms such as colic, diminished appetite, and constipation are also related to hypercalcemia and regular follow-up of serum calcium level is needed4). The pubertal growth spurt occurs 1 to 2 years earlier and the duration is shorter than normal, which may also contribute to short final adult height19,20). The incidence of early puberty in WBS is reported as high as 50%, but true precious puberty is rare6). In the present study, only 3 patients (2.9%) were diagnosed with central precocious puberty by a GnRH stimulation test and 2 of them required long term GnRH agonist therapy.
In this study, BMI-SDS was increased as patients grew older. Type 2 diabetes mellitus has been reported in 15% of adult patients with WBS17), but none were diagnosed in this study, probably because the number of adult patients was small.
Among the patients who were diagnosed with primary hypothyroidism, all of them underwent levothyroxine treatment. Careful monitoring of thyroid function is needed to determine the need for supplementation of thyroid hormone21). The prevalence of subclinical hypothyroidism is known to be inversely related to age22). Patients with congenital hypothyroidism are rare, but it could be the initial presentation leading to early diagnosis23). Immaturity of the hypothalamicpituitary-thyroid axis was suggested to be the cause, but the molecular mechanism of hypothyroidism in WBS remains uncertain24). In this study, 2 patients who underwent thyroid imaging showed hypoplasia of the thyroid gland. Up to 70% of patients with hypothyroidism showed morphological or volumetric abnormalities such as thyroid hypoplasia, therefore, thyroid imaging is recommended in all patients with WBS23,24). However, as in this study, autoimmune thyroiditis is rarely observed.
Symptomatic hypercalcemia in WBS is rare, but careful monitoring and appropriate management is required in the case of severe hypercalcemia. There are some reports of rebound hypercalcemia after treatment, emphasizing the importance of re-evaluating serum calcium levels during the follow-up period25,26). The cases in this study were treated with conventional therapies such as intravenous fluid and diuretics. Symptomatic hypercalcemia usually resolves during childhood6). Intravenous pamidronate could be useful in the case of intractable hypercalcemia by intravenous hydration with furosemide or hydrocortisone26). The gene causing hypercalcemia in WBS has not been identified yet. Overexpression of TRPC3 channels, which is known to be related to calcium transport in lymphocytes, was reported in a patient with WBS27). Increased 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 levels during the hypercalcemic phase was reported in a previous study, suggesting that abnormal synthesis of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 seems to be the cause of hypercalcemia in WBS28). Serum 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 levels were not elevated in our cohort, although it was measured in only 3 patients.
In conclusion, patients with WBS manifest various endocrine dysfunctions, such as postnatal growth retardation, central precocious puberty, hypothyroidism, and hypercalcemia. The severity and outcomes of their endocrine manifestations are heterogeneous. Therefore, long-term follow-up and longitudinal study is needed to develop monitoring guidelines for the endocrine problems and the disease-specific growth curve for patients with WBS in Korea.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant from the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (No. 2011-0019674).
References
1. Stromme P, Bjornstad PG, Ramstad K. Prevalence estimation of Williams syndrome. J Child Neurol 2002;17:269–271. PMID: 12088082.


2. Schubert C. The genomic basis of the Williams-Beuren syndrome. Cell Mol Life Sci 2009;66:1178–1197. PMID: 19039520.


3. Segura-Puimedon M, Sahun I, Velot E, Dubus P, Borralleras C, Rodrigues AJ, et al. Heterozygous deletion of the Williams-Beuren syndrome critical interval in mice recapitulates most features of the human disorder. Hum Mol Genet 2014;23:6481–6494. PMID: 25027326.



5. Li HH, Roy M, Kuscuoglu U, Spencer CM, Halm B, Harrison KC, et al. Induced chromosome deletions cause hypersociability and other features of Williams-Beuren syndrome in mice. EMBO Mol Med 2009;1:50–65. PMID: 20049703.



6. Committee on Genetics. American Academy of Pediatrics: Health care supervision for children with Williams syndrome. Pediatrics 2001;107:1192–1204. PMID: 11331709.

7. Palacios-Verdu MG, Segura-Puimedon M, Borralleras C, Flores R, Del Campo M, Campuzano V, et al. Metabolic abnormalities in Williams-Beuren syndrome. J Med Genet 2015;52:248–255. PMID: 25663682.


8. Partsch CJ, Dreyer G, Gosch A, Winter M, Schneppenheim R, Wessel A, et al. Longitudinal evaluation of growth, puberty, and bone maturation in children with Williams syndrome. J Pediatr 1999;134:82–89. PMID: 9880454.


9. Francke U. Williams-Beuren syndrome: genes and mechanisms. Hum Mol Genet 1999;8:1947–1954. PMID: 10469848.



10. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (KCDC). Korean Pediatric Society, Committee for the Development of Growth Standard for Korean Children and Adolescents. 2007 Korean children and adolescents growth standard: commentary for the development of 2007 growth chart [Internet]. Cheongju: KCDC, Division of Chronic Disease Surveillance. c2012;cited 2015 Sep 1. Available from: http://www.cdc.go.kr/CDC/info/CdcKrInfo0201.jsp?menuIds=HOME001-MNU0004-MNU0007-MNU0025&fid=28&q_type=&q_value=&cid=1235&pageNum=74.


11. Hyun SE, Lee BC, Suh BK, Chung SC, Ko CW, Kim HS, et al. Reference values for serum levels of insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 in Korean children and adolescents. Clin Biochem 2012;45:16–21. PMID: 22032863.


12. Greulich WW, Pyle SI. Radiographic atlas of skeletal development of the hand and wrist. 2nd ed. Stanford: Stanford University Press. 1959.


13. Abreu AP, Dauber A, Macedo DB, Noel SD, Brito VN, Gill JC, et al. Central precocious puberty caused by mutations in the imprinted gene MKRN3. N Engl J Med 2013;368:2467–2475. PMID: 23738509.



14. Corbetta C, Weber G, Cortinovis F, Calebiro D, Passoni A, Vigone MC, et al. A 7-year experience with low blood TSH cutoff levels for neonatal screening reveals an unsuspected frequency of congenital hypothyroidism (CH). Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2009;71:739–745. PMID: 19486019.


15. Leger J, Olivieri A, Donaldson M, Torresani T, Krude H, van Vliet G, et al. European Society for Paediatric Endocrinology consensus guidelines on screening, diagnosis, and management of congenital hypothyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2014;99:363–384. PMID: 24446653.




16. Pankau R, Partsch CJ, Gosch A, Oppermann HC, Wessel A. Statural growth in Williams-Beuren syndrome. Eur J Pediatr 1992;151:751–755. PMID: 1425797.


17. Morris CA, Demsey SA, Leonard CO, Dilts C, Blackburn BL. Natural history of Williams syndrome: physical characteristics. J Pediatr 1988;113:318–326. PMID: 2456379.


18. Eom HJ, Chung HJ, Kim SW, Kim YK. Clinical characteristics of children with Williams Syndrome according to age. J Korean Child Neurol Soc 2010;18:214–224.
19. Nogueira RJ, Zimmerman LF, Moreno YM, Comparini CR, Viana DV, Vieira TA, et al. Anthropometric and body-mass composition suggests an intrinsic feature in Williams-Beuren syndrome. Rev Assoc Med Bras 2011;57:681–685. PMID: 22249549.



20. Partsch CJ, Japing I, Siebert R, Gosch A, Wessel A, Sippell WG, et al. Central precocious puberty in girls with Williams syndrome. J Pediatr 2002;141:441–444. PMID: 12219071.



21. Selicorni A, Fratoni A, Pavesi MA, Bottigelli M, Arnaboldi E, Milani D. Thyroid anomalies in Williams syndrome: investigation of 95 patients. Am J Med Genet A 2006;140:1098–1101. PMID: 16596673.


22. Cambiaso P, Orazi C, Digilio MC, Loche S, Capolino R, Tozzi A, et al. Thyroid morphology and subclinical hypothyroidism in children and adolescents with Williams syndrome. J Pediatr 2007;150:62–65. PMID: 17188616.


23. Dimitriadou M, Christoforidis A, Sarri C, Gyftodimou Y, Athanassiou-Metaxa M. Congenital hypothyroidism as the initial presentation that led to the diagnosis of Williams syndrome. Gene 2012;494:102–104. PMID: 22198067.


24. Stagi S, Bindi G, Neri AS, Lapi E, Losi S, Jenuso R, et al. Thyroid function and morphology in patients affected by Williams syndrome. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2005;63:456–460. PMID: 16181239.


25. Helfrich AM, Philla KQ. Late-onset hypercalcemia in Williams-Beuren syndrome: importance of early and frequent screening and intervention. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 2015;28:425–428. PMID: 25332293.



26. Cagle AP, Waguespack SG, Buckingham BA, Shankar RR, Dimeglio LA. Severe infantile hypercalcemia associated with Williams syndrome successfully treated with intravenously administered pamidronate. Pediatrics 2004;114:1091–1095. PMID: 15466114.


27. Letavernier E, Rodenas A, Guerrot D, Haymann JP. Williams-Beuren syndrome hypercalcemia: is TRPC3 a novel mediator in calcium homeostasis? Pediatrics 2012;129:e1626–e1630. PMID: 22566418.


28. Garabedian M, Jacqz E, Guillozo H, Grimberg R, Guillot M, Gagnadoux MF, et al. Elevated plasma 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D concentrations in infants with hypercalcemia and an elfin facies. N Engl J Med 1985;312:948–952. PMID: 3838365.


Table 1
Clinical and endocrine characteristics of patients with central precocious puberty
Table 2
Nine patients (8.8%) with primary hypothyroidism
Table 3
Clinical and endocrine characteristics of patients with hypercalcemia
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 25 Crossref
- Scopus
- 11,796 View
- 218 Download
- Related articles in APEM
-
Neurocognitive and psychosocial profiles of children with Turner syndrome2023 December;28(4)
Endocrinal dysfunction in children with Down syndrome2022 March;27(1)
Effectiveness of growth hormone therapy in children with Noonan syndrome2020 September;25(3)
Growth hormone therapy in patients with Noonan syndrome2018 December;23(4)
Thyroid Dysfunction in Obese Children in Jeonju, Korea.2012 December;17(4)