 |
 |
- Search
| Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab > Volume 20(4); 2015 > Article |
|
Abstract
Hyponatremia and hyperkalemia in infancy can be attributed to various causes, originating from a variety of renal and genetic disorders. Pseudohypoaldosteronism type 1 (PHA1) is one of these disorders, causing mineralocorticoid resistance that results in urinary salt wasting, failure to thrive, metabolic acidosis, and dehydration. PHA1 is heterogeneous in etiology. Inactivating mutations in the NR3C2 gene (4q31.1), which encodes the mineralocorticoid receptor, causes a less severe autosomal dominant form that is restricted to the kidney, while mutations in the amiloride-sensitive epithelial sodium channel gene (alpha subunit=SCNN1A, 12p13; beta subunit=SCNN1b, 16p12.2-p12.1; gamma subunit=SCNN1G, 16p12) causes a more severe autosomal recessive form, which has systemic effects. Here we report a neonatal case of kidney restricted PHA1 (renal type of PHA1) who first showed laboratory abnormalities before obvious PHA1 manifestations, with two functional polymorphisms in the NR3C2 gene. This is the second genetically confirmed case in Korea and the first to show functional polymorphisms that have previously been reported in the literature.
Pseudohypoaldosteronism type 1 (PHA1) is a rare disorder showing resistance to mineralocorticoids and is characterized by urinary salt wasting, failure to thrive, dehydration, hyperkalemia and metabolic acidosis1). Laboratory evaluations show hyponatremia, hyperkalemia and metabolic acidosis combined with elevated plasma renin and aldosterone levels, which at times may be life-threatening in severe cases2). PHA1 is divided into two forms according to genetic etiology: an autosomal dominant type restricted to the kidney (renal type of PHA1, rPHA1)3) and a more severe autosomal recessive form that exhibits systemic symptoms (systemic PHA1, sPHA1)4). The rPHA1 is caused by various mutations in the NR3C2 gene on chromosome 4q31.1, which encodes the mineralocorticoid receptor (MR)3). To date, there have been several cases of PHA1 reported in Korea5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12) and only one case that has been genetically confirmed13). We report a new case of a neonate who first showed laboratory abnormalities before obvious PHA1 manifestations and who was diagnosed by molecular genetic tests to have two functional polymorphisms in the NR3C2 gene.
A one-day-old male was transferred to our neonatal intensive care unit from a local primary obstetric clinic several hours after birth due to respiratory difficulties. The patient was born at full term via caesarean section due to intermittent fetal heart deceleration during labor. There were no other remarkable perinatal complications or family history. Upon physical examination, the patient was seen to be large for his gestational age (physical profile: length, 55.0 cm [>95th percentile]; body weight, 4.4 g [>90th percentile]; head circumference, 37.5 cm [>95th percentile])14). No other notable physical anomaly could be seen. His chest x-ray showed overall decreased lung volume, and decreased breathing sounds upon auscultation proved the need for respiratory support. He was put on noninvasive continuous positive end expiratory pressure ventilation for two days, after which he was weaned from it and kept in the room air.
Initial laboratory values at the time of admission showed the following: serum sodium, 137.0 mmol/L; serum potassium, 6.0 mmol/L; serum chloride, 100.0 mmol/L; blood-ureanitrogen, 14 mg/dL; serum creatinine, 0.9 mg/dL; serum calcium, 9.0 mg/dL; and serum inorganic phosphate, 5.3 mg/dL. His venous blood gas analysis showed pH 7.26, PCO2 55.9 mmHg, bicarbonate 25.9 mmol/L and base excess -2.0 mmol/L, reflecting mild respiratory acidosis. The patient's feeding proved to be poor, as he showed signs of nausea and vomiting with abdominal distention, and considering his age and health status, we assessed the cause to be nonspecific. As he needed respiratory support, the patient was put on intravenous fluid replacement (sodium 15 mEq mixed in 500 mL of 10% dextrose solution; infusion rate differed depending on the oral intake amount, with total intake limited to the patient's maintenance volume), and after he was weaned from respiratory support, feeding amounts were slowly increased until full enteral feeding was possible; this occurred by day 8 of admission. Routine laboratory examination was done on day 7, and no specific abnormality was noted.
Despite improved feeding, the patient continued to experience weight loss from his birth weight of 4.4 kg to 3.6 kg, nearly a 20% loss (Fig. 1). However, his overall physical condition was good. On day 9, intravenous fluid supplementation was cut, and capillary/venous electrolytes and a blood gas analysis were taken on the day after cessation of fluid therapy (day 10) to check for laboratory abnormalities. Laboratory results showed hyponatremia (128.0 mmol/L) combined with hyperkalemia (>9.0 mmol/L), but no electrical abnormality was detected on his electrocardiogram. Metabolic acidosis with respiratory compensation could be seen on his venous blood gas analysis. The results of the patient's newborn screening test and tandem mass spectra taken two days earlier had not been reported yet. Under the impression of congenital adrenal hyperplasia, a hormone study was done. Until laboratory results could confirm the patient's diagnosis, treatment with hydrocortisone and fludrocortisone was initiated, and electrolyte imbalances were medically managed. The above treatment was continued until day 21, when the patient's hormone study results were reported. Contrary to our expectation, the patient's renin activity and aldosterone levels were elevated to 307.5 ng/mL/hr (normal range, 1.4-7.8 ng/mL/hr) and 3,853.0 ng/dL (normal range, 17.0-154.0 ng/dL) respectively, and the Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) level had decreased to 2.7 pg/mL (normal rang, 10.0-60.0 pg/mL) . These results were suggestive of pseudohypoaldosteronism.
To confirm the diagnosis, genetic analysis of the patient's NR3C2 gene was done, and the results revealed heterozygous c.538G>A (p.V180I) and c.-2C>G substitution (Fig. 2). The patient was taken off steroid treatment, and sodium replacement (15 mEq/kg/day) was started. He showed gradual weight gain, along with stable serum electrolyte levels, and was discharged from our institution at postnatal age 25 days. The patient is currently 17 months old, his body profile shows height and weight in the 10th percentile, and he is achieving adequate developmental milestones. He is on tapering doses of oral sodium supplementation (down to 9.5 mEq/kg/day) and is receiving regular check-ups including serum electrolyte levels at the outpatient department (Fig. 1). His latest hormone study results taken in May this year were as follows and has relatively normalized since his initial study results; renin activity, 21.2 ng/mL/hr; aldosterone, 172.4 ng/dL; and ACTH, 31.0 pg/mL (Table 1).
PHA1 is a rare congenital disorder caused by target organ resistance to mineralocorticoids1,2,15). Aldosterone, a key regulator of the final urinary sodium and potassium concentration in the distal nephron, acts by binding to the MR located in the epithelial cells of the distal tubules and collecting ducts of the nephron. It regulates sodium and potassium homeostasis by activating the basolateral Na+/K+ pumps and epithelial sodium channels (ENaCs)16). Resistance to aldosterone disturbs this regulation and causes hyponatremia and hyperkalemia17).
PHA1 is divided into two forms15,17), and depending on the mode of inheritance, it is distinguished as either the autosomal dominant or the autosomal recessive type. The autosomal dominant type is also known as the rPHA1, and it is due to inactivating mutations in the genes encoding the MR (NR3C2), which are located in the kidneys3). This type is followed by spontaneous remission over time16). The autosomal recessive form shows multiple target organ resistances, as it is caused by mutations in the amiloride-sensitive epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) gene subtypes which code the ENaCs located in the sweat glands, lungs and colon as well as in the kidney, thus resulting in the term, "systemic PHA1" (sPHA1)4,15,16). This type persists well into adulthood16).
In most reported cases, both types of PHA1 first present in infancy as clinical manifestations such as poor feeding, weight loss, dehydration and vomiting. As the clinical picture is similar to more common disorders such as congenital adrenal hyperplasia and adrenal hypoplasia, these are often misdiagnosed until elevated plasma renin activity and aldosterone are confirmed.
In our case, the patient fortunately presented first with laboratory abnormalities, and except for poor weight gain, the characteristic clinical manifestations of PHA1 did not appear. This led us to think of other disorders that would show a similar clinical picture, such as congenital adrenal hyperplasia or adrenal hypoplasia, and consequently, steroid treatment was initiated as soon as blood samples for the patient's hormone studies were taken. However, contrary to our expectations, the results of his hormone study showed high levels of renin activity and aldosterone, and this led to the diagnosis of PHA1.
A genetic molecular analysis of the patient revealed two heterozygous polymorphisms in the NR3C2 gene (c.538G>A(p.V180I) in exon 2, c.-2C>G which is located in the 5'-untranslated region of the NR3C2 gene, 2 nucleotides upstream of the first translation start site), confirming rPHA1 (Fig. 2). Although common among the healthy population, these polymorphisms have previously been reported to have roles in altering the function of the MR18,19). In a study by van Leeuwen et al.19), the G allele of the c.-2G>C variant of the MR, when compared with the C allele, showed in vitro to be associated with decreased levels of MR proteins and transcriptional activation and showed significantly higher plasma renin and aldosterone levels. On the other hand, in the presence of aldosterone, the C allele showed lower levels of basal cortisol concentrations. The substitution of the nucleotide C to G 2 nucleotides upstream of the coding region of the NR3C2 gene may account for the increased mineralocorticoid levels, probably due to decreased MR expression. Another known polymorphism of the NR3C2 gene results in an A to G substitution in the coding region, which changes an isoleucine to valine. Arai et al.18) showed that substitution of isoleucine 180 to valine in vitro affected MR transactivation function. This was also observed in our patient. Although both polymorphisms alone may not have enough influence on the MR, the combined effects of the two may account for the characteristic salt wasting in PHA1.
Although our patient was fortunate enough to have been in a hospitalized state before severe electrolyte imbalances could result in fatal consequences, other similar cases may not be as fortunate and may result in unexplained neonatal death. Geller et al.20) reported a high mortality rate in infants at risk for autosomal dominant PHA1, suggesting that the incidence of PHA1 may be higher than expected. These unexplained deaths may have been due to preceding electrolyte imbalances causing fatal results before the patient could show any signs of illness that would have led to appropriate and timely treatment. Several cases of PHA1 have been reported in Korea, although ours is the first in which the patient presented with potentially fatal levels of laboratory abnormalities with only minor clinical presentations that could be mistaken for other nonfatal causes. As functional polymorphisms alone may result only in subtle and rarely noticeable symptoms, one should be on the alert for overt PHA manifestations, should multiple polymorphisms cause cumulative effects, as this may lead to sudden death that may seem unexplainable. PHA1 should be considered in families with histories of sudden infant deaths, and if possibilities exist, gene studies may be performed to check for polymorphisms.
This case is the first in Korea to identify existing frequent polymorphisms of the MR that may have cumulative effects on the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone axis. Genotyping common polymorphisms of the MR could help in identifying patients at risk of PHA1, which, if not treated in time, may have fatal consequences.
References
1. Cheek DB, Perry JW. A salt wasting syndrome in infancy. Arch Dis Child 1958;33:252–256. PMID: 13545877.



3. Geller DS, Rodriguez-Soriano J, Vallo Boado A, Schifter S, Bayer M, Chang SS, et al. Mutations in the mineralocorticoid receptor gene cause autosomal dominant pseudohypoaldosteronism type I. Nat Genet 1998;19:279–281. PMID: 9662404.


4. Chang SS, Grunder S, Hanukoglu A, Rosler A, Mathew PM, Hanukoglu I, et al. Mutations in subunits of the epithelial sodium channel cause salt wasting with hyperkalaemic acidosis, pseudohypoaldosteronism type 1. Nat Genet 1996;12:248–253. PMID: 8589714.



5. Kwon YS, Shin HG, Ahn MS, Kim HB. A case of pseudohypoaldosteronism. J Korean Pediatr Soc 1992;35:984–988.
6. Lee JE, Seo JW, Lee SJ. Two cases of pseudohypoaldosteronism type I. J Korean Pediatr Soc 1994;37:122–128.
7. Lee R, Kim SY, Choi SD, Chung SY, Kang JH, Lee BC. Two male siblings with pseudohypoaldosteronism type I. J Korean Pediatr Soc 1994;37:262–268.
8. Kang IN, Lee JW, Bang JG, Lee DB. A case of pseudohypoaldosteronism. J Korean Pediatr Soc 1995;38:1160–1163.
9. Kim SJ, Lim PJ, Ban SH, Lee DH, Jin DK, Song SM, et al. Two cases with pseudohypoaldosteronism. J Korean Soc Pediatr Endocrinol 2000;5:215–219.
10. Choi J, Hahn H, Park YS, You HW. A case of transient pseudohypoaldosteronism secondary to ureteropelvic junction obstruction. J Korean Soc Pediatr Nephrol 2004;8:91–95.
11. Han SB, Lim CH, Lee KY, Kim JS, Kim WH, Uhm M. A case of pseudohypoaldosteronism type l diagnosed after Infancy. J Korean Soc Pediatr Endocrinol 2007;12:82–86.
12. Ahn SY, Shin SM, Kim KA, Lee YK, Ko SY. Pseudohypoaldosteronism in a premature neonate with severe polyhydramnios in utero. Korean J Pediatr 2009;52:376–379.

13. Lee SE, Jung YH, Han KH, Lee HK, Kang HG, Ha IS, et al. A case of pseudohypoaldosteronism type 1 with a mutation in the mineralocorticoid receptor gene. Korean J Pediatr 2011;54:90–93. PMID: 21503203.



14. Ahn HS. Hong Chang Yee textbook of pediatrics. 10th ed. Seoul: Mirae N Co.. 2012;pp 1240.
16. Amin N, Alvi NS, Barth JH, Field HP, Finlay E, Tyerman K, et al. Pseudohypoaldosteronism type 1: clinical features and management in infancy. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep 2013;2013:130010. PMID: 24616761.



18. Arai K, Nakagomi Y, Iketani M, Shimura Y, Amemiya S, Ohyama K, et al. Functional polymorphisms in the mineralocorticoid receptor and amirolide-sensitive sodium channel genes in a patient with sporadic pseudohypoaldosteronism. Hum Genet 2003;112:91–97. PMID: 12483305.


19. van Leeuwen N, Caprio M, Blaya C, Fumeron F, Sartorato P, Ronconi V, et al. The functional c.-2G>C variant of the mineralocorticoid receptor modulates blood pressure, renin, and aldosterone levels. Hypertension 2010;56:995–1002. PMID: 20855654.


20. Geller DS, Zhang J, Zennaro MC, Vallo-Boado A, Rodriguez-Soriano J, Furu L, et al. Autosomal dominant pseudohypoaldosteronism type 1: mechanisms, evidence for neonatal lethality, and phenotypic expression in adults. J Am Soc Nephrol 2006;17:1429–1436. PMID: 16611713.


Fig. 1
Serum sodium and potassium levels. The patient initially showed normal electrolyte levels immediately after birth. On the 10th day after birth, serum sodium was 128.0 mmol/L, and potassium levels increased to 9.0 mmol/L. Treatment to lower the patient's potassium level was initiated simultaneously and was continued until electrolyte levels normalized*, and sodium supplementation was started†.
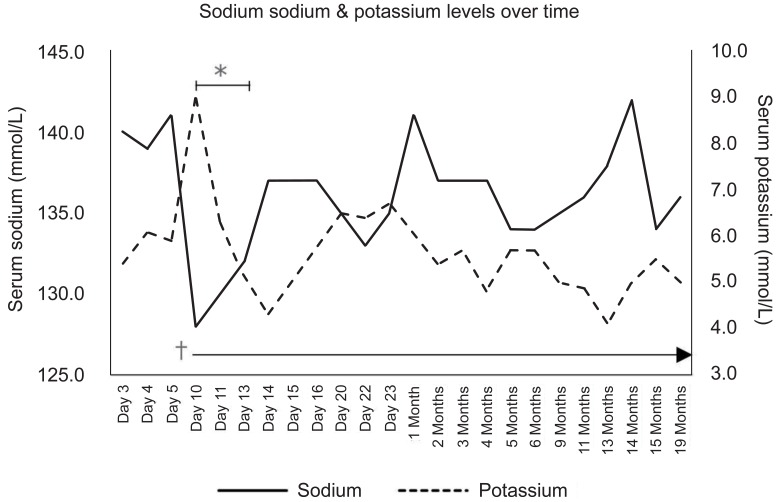
Fig. 2
Partial gene sequencing of the patient's NR3C2 gene. (A) The patient also showed a heterozygous c.-2C>G substitution in the 5'-UT region of the NR3C2 gene, 2 nucleotides upstream of the first translation start site. (B) The patient had a heterozygous c.538G>A substitution in exon 2, which results in an isoleucine changing to valine. G, guanine; A, adenine; C, cytosine; UT, untranslated.
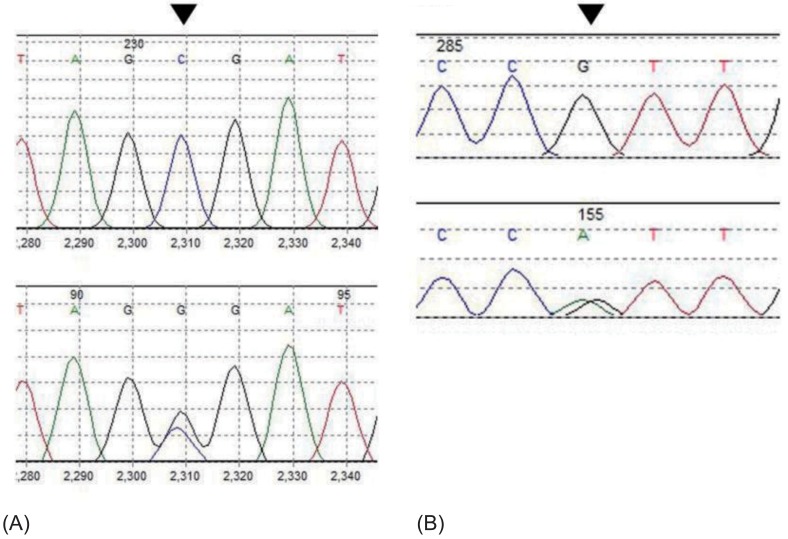
Table 1
Serial hormone study results
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 2 Crossref
- Scopus
- 7,898 View
- 132 Download
- Related articles in APEM





