 |
 |
- Search
| Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab > Volume 20(1); 2015 > Article |
|
Abstract
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) is one of the most common inherited metabolic disorders. It comprises a group of autosomal recessive disorders caused by the mutations in the genes encoding for steroidogenic enzymes that involved cortisol synthesis. More than 90% of cases are caused by a defect in the enzyme 21-hydroxylase. Four other enzyme deficiencies (cholesterol side-chain cleavage, 17╬▒-hydroxylase [P450c17], 11╬▓-hydroxylase [P450c11╬▓], 3╬▓-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase) in the steroid biosynthesis pathway, along with one cholesterol transport protein defect (steroidogenic acute regulatory protein), and one electrontransfer protein (P450 oxidoreductase) account for the remaining cases. The clinical symptoms of the different forms of CAH result from the particular hormones that are deficient and those that are produced in excess. A characteristic feature of CAH is genital ambiguity or disordered sex development, and most variants are associated with glucocorticoid deficiency. However, in the rare forms of CAH other than 21-hydroxylase deficiency so-called "atypical CAH", the clinical and hormonal phenotypes can be more complicated, and are not well recognized. This review will focus on the atypical forms of CAH, including the genetic analyses, and phenotypic correlates.
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) is one of the most common inherited metabolic disorders and is associated with significant morbidity and mortality in affected children. It comprises a group of autosomal recessive disorders caused by the mutations in the genes encoding for steroidogenic enzymes that involved cortisol synthesis. Impaired cortisol secretion results in hypersecretion of corticotropin-releasing hormone and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and consequent hyperplasia of the adrenal glands. The clinical phenotypes and biochemical characteristics depend on the specific enzymatic defect. There is a broad clinical spectrum of this disorder. In most forms of CAH, it can be fatal if not diagnosed early in infancy1).
The adrenal cortex is the production site for three classes of steroid hormones: mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, and sex hormones. The cortex is divided into three zones by different cellular arrangements, each one functionally distinct due to the enzymes required for different hormone production. The outer zona glomerulosa does not express 17╬▒-hydroxylase (P450c17)2) and hence produces 17-deoxysteroids leading to aldosterone (the most potent mineralocorticoid), and is regulated primarily by the renin/angiotensin system. The middle zona fasciculata expresses the 17╬▒-hydroxylase activity but very little of the 17,20-lyase activity of P450c17, and hence produces 21-carbon, 17-hydroxysteroids, leading to cortisol under the influence of ACTH. The inner zona reticularis expresses both the 17╬▒-hydroxylase and 17,20-lyase activities of P450c17, and hence produce the 19-carbon 17-hydroxy steroid dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), the precursor of sex steroids1,3).
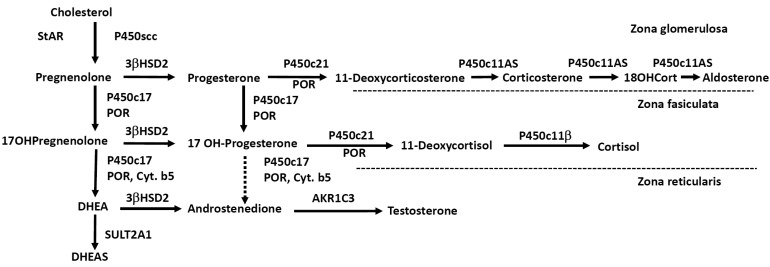
ACTH regulates steroidogenesis (chronic regulation) by inducing the transcription of genes encoding various steroidogenic enzymes, but acute regulation is at the level of cholesterol access to cholesterol side-chain cleavage (P450scc). The steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR) facilitates the movement of cholesterol into mitochondria, where it is converted to pregnenolone by P450scc4). Simplified diagram of adrenal steroidogenic pathways was shown in Fig. 1.
There have been nationwide newborn screening programs for CAH in only a few countries in Asia, although the recent pilot study suggested the high prevalence of CAH in Southeast Asian countries5,6). More than 90% of cases are caused by a defect in the enzyme 21-hydroxylase (P450c21). Four other enzyme deficiencies in the steroid biosynthesis pathway (P450scc, P450c17, 11╬▓-hydroxylase [P450c11╬▓], 3╬▓-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase [3╬▓HSD]), along with one cholesterol transport protein defect (StAR), and one electron-transfer protein (P450 oxidoreductase; POR) account for the remaining cases. In these uncommon forms of CAH, the clinical and hormonal phenotypes can be complicated, and are not widely recognized by endocrinologists or pediatricians.
The clinical symptoms of the different forms of CAH result from the particular hormones that are deficient and those that are produced in excess. A characteristic feature of CAH is genital ambiguity or disordered sex development (DSD), and all variants are associated with glucocorticoid deficiency. Each variant of CAH is summarized in Table 1. In this review, we focus on the molecular genetic basis of the variant forms of CAH other than 21-hydroxylase so-called "atypical CAH", including the genetic analysis, and phenotypic correlates.
Congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia is the most severe form of CAH in which the synthesis of all adrenal and gonadal steroid hormones is impaired and leads to the accumulation of cholesterol esters7,8). The true incidence of lipoid CAH is unknown, but it is clearly much higher in Japanese, Korean and Palestinian population. Patients with classic lipoid CAH usually present with adrenal failure and salt wasting, beginning within the first few months of life, and have female external genitalia irrespective of genetic sex1).
Early clinical hormonal studies and incubations of affected tissue in vitro with various precursors identified a defect in the conversion of cholesterol to pregnenolone, so that the disorder was initially called "20,22 desmolase deficiency" as it was thought to result from a defect in the enzyme system converting cholesterol to pregnenolone; this enzyme was later identified as mitochondrial P450scc. However, in 1995 it was found that lipoid CAH results from mutations in the gene encoding the StAR7). StAR facilitates the movement of cholesterol into mitochondria, where it is converted to pregnenolone by P450scc4). StAR is expressed in the adrenals and gonads but not in the placenta9). Because placental production of progesterone is essential for the maintenance of human pregnancy, mutations in P450scc were thought to be incompatible with term gestation. Nevertheless, beginning in 2001 several patients with defects in CYP11A1 gene causing P450scc deficiency have been reported10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17). Most of these cases were caused by severe loss-of function mutations and presented with severe, early onset adrenal failure and complete phenotypic 46,XY sex reversal in genetic males14), although patients with late-onset nonclassic disease have been reported15,16,17,18). Thus, both of the defects of StAR and P450scc are now considered to be responsible for lipoid CAH, but most lipoid CAH may be caused by the mutations in the StAR gene.
More than 40 StAR mutations causing classic lipoid CAH have been described, but very few partial loss-of-function mutations have been reported19,20,21). The mutations are present in all exons. The mutations in intronic region are also found. The mutations causing premature translational termination or altering of the StAR reading frame are common, and they substantially alter the structure of the StAR protein. All missense mutations are found in the carboxy-terminal 40% of the amino acid StAR protein22). The Q258X mutation in exon 7 is very common in Japanese and Korean23,24). In Japanese this mutation is identified in 62% of the alleles and in over 80% of the patients. Other genetic clusters are found among Palestinian Arabs, most of whom carry the mutation R182L8); in eastern Saudi Arabia, carrying R182H25); and in parts of Switzerland, carrying the mutation L260P26).
Nonclassic lipoid CAH is a recently recognized disorder caused by StAR mutations that retain partial activity19). Affected individuals can present with later onset of adrenal insufficiency resembling nonautoimmune Addison disease with only mildly disordered sexual development or normal development with hypergonadotropic hypogonadism19,20,21). We recently reported four patients with nonclassic/atypical lipoid CAH and demonstrated that there is a broad clinical spectrum of StAR mutations21). While there is some variability in these biochemical assays, it seems that 10%-20% activity will dramatically alter the classic phenotype21). The R188C mutation was found in patients from Thailand, Canada, Jordan, India and Pakistan19,20,21), suggesting a recurrent mutation. To date, most patients with non-classic lipoid CAH carry R188C, although other mutations can cause this phenotype19,20,21).
3╬▓HSD or ╬ö5ŌåÆ╬ö4-isomerase is a 42 kDa microsomal enzyme catalyzes steroidogenic reactions: the conversion of the hydroxyl group to a keto group on carbon 3 and the isomerization of ╬ö5 steroids precursors into ╬ö4 ketosteroids27). Therefore, 3╬▓HSD is responsible for the conversion of pregnenolone to progesterone, 17╬▒-hydroxypregnenolone (17OHPreg) to 17╬▒-hydroxyprogesterone (17OHP), DHEA to androstenedione, and androstenediol to testosterone. Thus, 3╬▓HSD is an essential enzyme for biosynthesis of all classes of active steroid hormones including aldosterone, and cortisol in adrenal cortex, and sex steroids in adrenals and gonads.
In humans, there are two closely linked genes HSD3B1 and HSD3B2 located on chromosome 1 encoded two isoforms of 3╬▓HSD28). The type 1 enzyme (3╬▓HSD1) encoded by HSD3B1 is primarily expressed in placenta, mammary gland, liver, skin and some other tissues29). 3╬▓HSD1 is required for placental progesterone synthesis during pregnancy. Mutations in HSD3B1 gene have never been described, presumably because these would cause a spontaneous abortion due to lack of placental progesterone synthesis. In contrast, the type 2 enzyme (3╬▓HSD2) encoded by HSD3B2 gene is predominantly expressed in the adrenals and gonads29). Defects in HSD3B2 gene causes 3╬▓HSD deficiency, which is a rare form of CAH, and can be fatal if not diagnosed early in infancy30).
The clinical spectrum of 3╬▓HSD deficiency ranges from saltwasting to non-salt-wasting forms. In its classic form, 3╬▓HSD deficiency causes various degrees of salt-wasting in both sexes. In genetic males, 3╬▓HSD deficiency in the testes impairs testosterone biosynthesis from early fetal life, so that these males have undervirilization of the external genitalia, and usually present at birth with severe hypospadias and micropenis. By contrast, genetic females have normal female genitalia or slightly virilized genitalia such as isolated clitoromegaly, because the fetal adrenal overproduces large amounts of DHEA, which can be converted to testosterone by extraadrenal 3╬▓HSD11,31). In this way, the presence of peripheral 3╬▓HSD1 activity often complicates the hormonal diagnosis of this disorder in that very high 17OHPreg levels can be converted extra-adrenally to 17OHP confuses the diagnosis as 21-hydroxylase deficiency31,32).
Mild forms of 3╬▓HSD deficiency cause premature acne, premature pubarche, and growth acceleration in children33) and a late onset variant manifesting with hirsutism, menstrual disorder, and polycystic ovaries in young women34,35). The newly proposed hormonal criteria for diagnosis for 3╬▓HSD deficiency were elevated basal and ACTH-stimulated 17OHPreg and 17OHPreg to cortisol ratios, typically exceed 10 standard deviations above the mean36). These criteria were revised based on genotype-proven patients.
To date approximately 40 mutations have been identified in the HSD3B2 gene in patients suffering from classical 3╬▓HSD deficiency. In most cases, the functional consequences of HSD3B2 mutations are in close agreement with the severity of the clinical manifestation. However, the in vitro 3╬▓HSD activities alone cannot be used to predict the degree of male undervirilization31).
11╬▓-hydroxylase deficiency (11OHD) accounts for about 5%-8% of CAH in people of European ancestry but accounts for about 15% of cases in both Muslim and Jewish Middle Eastern populations1). P450c11╬▓ catalyses conversion of 11-deoxycortisol to cortisol, representing the final step in cortisol biosynthesis. The enzyme also catalyses the monooxygenase reaction converting 11-deoxycorticosterone (DOC) to corticosterone. Thus, deficient P450c11╬▓ activity results in decreased cortisol secretion and accumulation of 11-deoxycortisol and the mineralocorticoid precursor DOC. Thus, patients can subsequently suffer from significant hypertension, a hallmark feature of this CAH variant. Accumulated precursors are shunted into the androgen synthesis pathway, leading to hyperandrogenism. Classic 11OHD most commonly results in 46,XX DSD with severe virilization of the external genitalia, and precocious pseudopuberty in both sexes. Newborns may also have elevated concentrations of 17OHP, which accumulates two steps behind the enzymatic block, so that P450c11╬▓ deficiency may be detected in newborn screening for P450c21 deficiency37). The diagnosis is established by elevated basal concentrations of DOC and 11-deoxycortisol, which hyperrespond to cosyntropin. 11OHD is caused by mutations in the CYP11B1 gene. At present, over 50 CYP11B1-inactivating mutations are described. Most are missense and nonsense mutations, but splice-site mutations, small deletions, small insertions, and complex rearrangements have also been detected38,39,40). The vast majority of mutations are associated with classic 11OHD, and only a few mutations causing nonclassic 11OHD have been described in otherwise asymptomatic women with hirsutism, and menstrual irregularities41,42).
Generally, the CYP11B1 gene is specifically amplified avoiding simultaneous amplification of homologous CYP11B2 sequences. In the majority of cases, molecular genetic analysis is not difficult. However, special cases are reported, such as an unequal crossing-over between the CYP11B2 and the CYP11B1 genes as a cause of 11OHD43).
P450c17 is the single microsomal cytochrome P450 enzyme that catalyzes both the 17╬▒-hydroxylation required to produce the 17 hydroxy 21-carbon precursors of cortisol, 17OHPreg and 17OHP, and the 17,20-lyase activity needed to produce 19-carbon precursors of sex steroids44). P450c17 is encoded by CYP17A1 gene, consisting of eight exons and located on chromosome 10q24.345). CYP17A1 mutations cause P450c17 deficiency, a rare form of CAH characterized by sexual infantilism, 46,XY sex reversal, hypertension and high ratios of C21 to C19 steroids. The lack of P450c17 activity disrupts cortisol secretion, driving the compensatory overproduction of a glucocorticoid, corticosterone, and a mineralocorticoid, deoxycorticosterone, causing hypertension and hypokalemia1,46). Rare patients may also have isolated 17,20 lyase deficiency, characterized by low C19 steroids with normal cortisol47,48).
Over 70 CYP17A1-inactivating mutations have been identified. There is no evidence of a hot spot in most large populations. Therefore, sequencing of the entire coding region is usually necessary. Exceptions have been described in the some population, where mutations appear recurrently (1) a duplication of four nucleotides causing a frameshift is found among descendents of Dutch Frieslanders; (2) in-frame deletion of residues 487-489 is found throughout Southeast Asia; (3) a deletion of phenylalanine at position 53 or 54; and (4) the common W406R and R362C mutations, found among Brazilians of Spanish and Portuguese ancestry, respectively1).
POR deficiency is a unique and newly recognized form of CAH, biochemically manifesting with apparent combined P450c17 and P450c21 deficiency. POR transfers electrons from reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) to all microsomal (type II) cytochrome P450 enzymes, including three steroidogenic enzymes: P450c17 (17╬▒-hydroxylase/17,20 lyase), P450c21 (21-hydroxylase), and P450aro (aromatase)1). Although disruption of the POR gene in mice causes gross disorders of embryogenesis and embryonic lethality, in 2004 Fluck et al.49) reported POR mutations in three children with ambiguous genitalia and skeletal malformations (Antley-Bixler syndrome, ABS) and in a phenotypically normal adult woman with primary amenorrhea and polycystic ovaries. The majority of patients with POR deficiency described to date have also had the ABS phenotype, characterized by craniosynostosis, radioulnar or radiohumeral synostosis, bowed femora, and other variable skeletal disorders1,50). POR deficiency can cause ambiguous genitalia in both sexes. 46,XY males are typically undervirilized because decreased 17,20-lyase activity reduces androgen synthesis. 46,XX females are frequently virilized at birth, but this virilization is not progressive postnatally. There are two possible mechanisms for this virilization. First, because placental aromatase (P450aro) requires POR, a defect in this placental aromatase activity, either from mutation of POR or P450aro itself, will permit large amounts of fetal C19 steroids to enter and virilize the mother and the female fetus. Second, it appears to involve the "backdoor pathway" to fetal androgen production, in which 21-carbon steroid precursors are 5╬▒-reduced and ultimately converted to dihydrotestosterone, bypassing the conventional precursors androstenedione and testosterone1,50).
The human POR gene consists of 16 exons, spanning approximately 70 kb on chromosome 7q11.2. The overall incidence of POR deficiency in the general population remains unclear. However, over 50 POR mutations have now been described, suggesting that this disorder may be relatively common. There is the great variability in the clinical and hormonal findings in POR deficiency. Some patients with milder POR mutations do not have ABS, and the steroidogenic defect may present as hypogonadism and/or infertility49,50,51,52). Two mutations are especially common: A287P, the predominant mutation in patients of European ancestry, and R457H, the predominant mutation in patients of Japanese ancestry53,54,55). The genotype-phenotype correlation is not fully established yet55,56), and future studies are needed.
There is a broad spectrum of the clinical and hormonal phenotypes of CAH depending on the specific enzymatic defect. The diagnosis remains a challenge in patients with atypical forms of CAH and requires thorough clinical and hormonal work-up. Lifelong treatment with steroids is required for most patients. Confirmation of the diagnosis by genetic analysis is of clinical importance.
Acknowledgments
The author is grateful to Drs. Walter L. Miller (University of California, San Francisco, CA, USA) and Vorasuk Shotelersuk (Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand) for their excellent mentorship. T.S. was supported by Ratchadapiseksompotch funds from Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, and the Thailand Research Fund.
References
1. Miller WL, Auchus RJ. The molecular biology, biochemistry, and physiology of human steroidogenesis and its disorders. Endocr Rev 2011;32:81ŌĆō151. PMID: 21051590.




2. Suzuki T, Sasano H, Takeyama J, Kaneko C, Freije WA, Carr BR, et al. Developmental changes in steroidogenic enzymes in human postnatal adrenal cortex: immunohistochemical studies. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2000;53:739ŌĆō747. PMID: 11155097.


3. Miller WL. Minireview: regulation of steroidogenesis by electron transfer. Endocrinology 2005;146:2544ŌĆō2550. PMID: 15774560.



4. Stocco DM, Clark BJ. Regulation of the acute production of steroids in steroidogenic cells. Endocr Rev 1996;17:221ŌĆō244. PMID: 8771357.


5. Janejai N, Krasao P, Phansang J, Pankarnjanato R, Charoensiriwatana W. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia: should nationwide screening be implemented in Thailand. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 2003;34(Suppl 3):170ŌĆō173. PMID: 15906728.
6. Somboonnithiphol K, Panamonta O, Kiatchoosakun P, Jirapradittha J, Panamonta M, Lumbiganon P. Newborn screening for congenital adrenal hyperplasia in Srinagarind Hospital, Khon Kaen University, Thailand. Asian Biomed 2011;5:855ŌĆō859.
7. Lin D, Sugawara T, Strauss JF 3rd, Clark BJ, Stocco DM, Saenger P, et al. Role of steroidogenic acute regulatory protein in adrenal and gonadal steroidogenesis. Science 1995;267:1828ŌĆō1831. PMID: 7892608.


8. Bose HS, Sugawara T, Strauss JF 3rd, Miller WL. International Congenital Lipoid Adrenal Hyperplasia Consortium. The pathophysiology and genetics of congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia. N Engl J Med 1996;335:1870ŌĆō1878. PMID: 8948562.


9. Bose HS, Whittal RM, Baldwin MA, Miller WL. The active form of the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein, StAR, appears to be a molten globule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1999;96:7250ŌĆō7255. PMID: 10377400.



10. Tajima T, Fujieda K, Kouda N, Nakae J, Miller WL. Heterozygous mutation in the cholesterol side chain cleavage enzyme (p450scc) gene in a patient with 46,XY sex reversal and adrenal insufficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001;86:3820ŌĆō3825. PMID: 11502818.


11. Katsumata N, Ohtake M, Hojo T, Ogawa E, Hara T, Sato N, et al. Compound heterozygous mutations in the cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme gene (CYP11A) cause congenital adrenal insufficiency in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002;87:3808ŌĆō3813. PMID: 12161514.


12. Hiort O, Holterhus PM, Werner R, Marschke C, Hoppe U, Partsch CJ, et al. Homozygous disruption of P450 side-chain cleavage (CYP11A1) is associated with prematurity, complete 46,XY sex reversal, and severe adrenal failure. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005;90:538ŌĆō541. PMID: 15507506.


13. al Kandari H, Katsumata N, Alexander S, Rasoul MA. Homozygous mutation of P450 side-chain cleavage enzyme gene (CYP11A1) in 46, XY patient with adrenal insufficiency, complete sex reversal, and agenesis of corpus callosum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006;91:2821ŌĆō2826. PMID: 16705068.



14. Kim CJ, Lin L, Huang N, Quigley CA, AvRuskin TW, Achermann JC, et al. Severe combined adrenal and gonadal deficiency caused by novel mutations in the cholesterol side chain cleavage enzyme, P450scc. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008;93:696ŌĆō702. PMID: 18182448.




15. Rubtsov P, Karmanov M, Sverdlova P, Spirin P, Tiulpakov A. A novel homozygous mutation in CYP11A1 gene is associated with late-onset adrenal insufficiency and hypospadias in a 46,XY patient. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2009;94:936ŌĆō939. PMID: 19116240.



16. Sahakitrungruang T, Tee MK, Blackett PR, Miller WL. Partial defect in the cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme P450scc (CYP11A1) resembling nonclassic congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2011;96:792ŌĆō798. PMID: 21159840.




17. Tee MK, Abramsohn M, Loewenthal N, Harris M, Siwach S, Kaplinsky A, et al. Varied clinical presentations of seven patients with mutations in CYP11A1 encoding the cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme, P450scc. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2013;98:713ŌĆō720. PMID: 23337730.



18. Parajes S, Kamrath C, Rose IT, Taylor AE, Mooij CF, Dhir V, et al. A novel entity of clinically isolated adrenal insufficiency caused by a partially inactivating mutation of the gene encoding for P450 side chain cleavage enzyme (CYP11A1). J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2011;96:E1798ŌĆōE1806. PMID: 21880796.


19. Baker BY, Lin L, Kim CJ, Raza J, Smith CP, Miller WL, et al. Nonclassic congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia: a new disorder of the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein with very late presentation and normal male genitalia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006;91:4781ŌĆō4785. PMID: 16968793.




20. Metherell LA, Naville D, Halaby G, Begeot M, Huebner A, Nurnberg G, et al. Nonclassic lipoid congenital adrenal hyperplasia masquerading as familial glucocorticoid deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2009;94:3865ŌĆō3871. PMID: 19773404.




21. Sahakitrungruang T, Soccio RE, Lang-Muritano M, Walker JM, Achermann JC, Miller WL. Clinical, genetic, and functional characterization of four patients carrying partial loss-of-function mutations in the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR). J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2010;95:3352ŌĆō3359. PMID: 20444910.




22. Fujieda K, Okuhara K, Abe S, Tajima T, Mukai T, Nakae J. Molecular pathogenesis of lipoid adrenal hyperplasia and adrenal hypoplasia congenita. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 2003;85:483ŌĆō489. PMID: 12943739.


23. Nakae J, Tajima T, Sugawara T, Arakane F, Hanaki K, Hotsubo T, et al. Analysis of the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR) gene in Japanese patients with congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia. Hum Mol Genet 1997;6:571ŌĆō576. PMID: 9097960.


24. Kim CJ. Congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 2014;19:179ŌĆō183. PMID: 25654062.



25. Chen X, Baker BY, Abduljabbar MA, Miller WL. A genetic isolate of congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia with atypical clinical findings. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005;90:835ŌĆō840. PMID: 15546900.


26. Fluck CE, Maret A, Mallet D, Portrat-Doyen S, Achermann JC, Leheup B, et al. A novel mutation L260P of the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein gene in three unrelated patients of Swiss ancestry with congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005;90:5304ŌĆō5308. PMID: 15985476.


27. Lorence MC, Murry BA, Trant JM, Mason JI. Human 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/delta 5ŌåÆ4isomerase from placenta: expression in nonsteroidogenic cells of a protein that catalyzes the dehydrogenation/isomerization of C21 and C19 steroids. Endocrinology 1990;126:2493ŌĆō2498. PMID: 2139411.



28. Lorence MC, Corbin CJ, Kamimura N, Mahendroo MS, Mason JI. Structural analysis of the gene encoding human 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/delta 5ŌåÆ4-isomerase. Mol Endocrinol 1990;4:1850ŌĆō1855. PMID: 2082186.


29. Lachance Y, Luu-The V, Labrie C, Simard J, Dumont M, de Launoit Y, et al. Characterization of human 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/delta 5-delta 4-isomerase gene and its expression in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem 1990;265:20469ŌĆō20475. PMID: 2243100.


30. Bongiovanni AM. The adrenogenital syndrome with deficiency of 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. J Clin Invest 1962;41:2086ŌĆō2092. PMID: 13968789.



31. Simard J, Ricketts ML, Gingras S, Soucy P, Feltus FA, Melner MH. Molecular biology of the 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/delta5-delta4 isomerase gene family. Endocr Rev 2005;26:525ŌĆō582. PMID: 15632317.



32. Jeandron DD, Sahakitrungruang T. A novel homozygous Q334X mutation in the HSD3B2 gene causing classic 3╬▓-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency: an unexpected diagnosis after a positive newborn screen for 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Horm Res Paediatr 2012;77:334ŌĆō338. PMID: 22343390.


33. Moisan AM, Ricketts ML, Tardy V, Desrochers M, M├®barki F, Chaussain JL, et al. New insight into the molecular basis of 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency: identification of eight mutations in the HSD3B2 gene eleven patients from seven new families and comparison of the functional properties of twenty-five mutant enzymes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999;84:4410ŌĆō4425. PMID: 10599696.

34. Chang YT, Kulin HE, Garibaldi L, Suriano MJ, Bracki K, Pang S. Hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis function in pubertal male and female siblings with glucocorticoidt re ated nonsalt-wasting 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1993;77:1251ŌĆō1257. PMID: 8077318.


35. Sanchez R, Rheaume E, Laflamme N, Rosenfield RL, Labrie F, Simard J. Detection and functional characterization of the novel missense mutation Y254D in type II 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3 beta HSD) gene of a female patient with nonsalt-losing 3 beta HSD deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1994;78:561ŌĆō567. PMID: 8126127.


36. Mermejo LM, Elias LL, Marui S, Moreira AC, Mendonca BB, de Castro M. Refining hormonal diagnosis of type II 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency in patients with premature pubarche and hirsutism based on HSD3B2 genotyping. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005;90:1287ŌĆō1293. PMID: 15585552.


37. Peter M, Janzen N, Sander S, Korsch E, Riepe FG, Sander J. A case of 11beta-hydroxylase deficiency detected in a newborn screening program by second-tier LC-MS/MS. Horm Res 2008;69:253ŌĆō256. PMID: 18204274.

38. White PC, Dupont J, New MI, Leiberman E, Hochberg Z, Rosler A. A mutation in CYP11B1 (Arg-448----His) associated with steroid 11 beta-hydroxylase deficiency in Jews of Moroccan origin. J Clin Invest 1991;87:1664ŌĆō1667. PMID: 2022736.



39. Nimkarn S, New MI. Steroid 11beta-hydroxylase deficiency congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2008;19:96ŌĆō99. PMID: 18294861.


40. Zhu YS, Cordero JJ, Can S, Cai LQ, You X, Herrera C, et al. Mutations in CYP11B1 gene: phenotype-genotype correlations. Am J Med Genet A 2003;122A:193ŌĆō200. PMID: 12966519.


41. Joehrer K, Geley S, Strasser-Wozak EM, Azziz R, Wollmann HA, Schmitt K, et al. CYP11B1 mutations causing non-classic adrenal hyperplasia due to 11 beta-hydroxylase deficiency. Hum Mol Genet 1997;6:1829ŌĆō1834. PMID: 9302260.



42. Reisch N, Hogler W, Parajes S, Rose IT, Dhir V, Gotzinger J, et al. A diagnosis not to be missed: nonclassic steroid 11╬▓-hydroxylase deficiency presenting with premature adrenarche and hirsutism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2013;98:E1620ŌĆōE1625. PMID: 23940125.


43. Hampf M, Dao NT, Hoan NT, Bernhardt R. Unequal crossing-over between aldosterone synthase and 11beta-hydroxylase genes causes congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001;86:4445ŌĆō4452. PMID: 11549691.

44. Chung BC, Picado-Leonard J, Haniu M, Bienkowski M, Hall PF, Shively JE, et al. Cytochrome P450c17 (steroid 17 alpha-hydroxylase/17,20 lyase): cloning of human adrenal and testis cDNAs indicates the same gene is expressed in both tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1987;84:407ŌĆō411. PMID: 3025870.



45. Picado-Leonard J, Miller WL. Cloning and sequence of the human gene for P450c17 (steroid 17 alpha-hydroxylase/ 17,20 lyase): similarity with the gene for P450c21. DNA 1987;6:439ŌĆō448. PMID: 3500022.


46. Sahakitrungruang T, Tee MK, Speiser PW, Miller WL. Novel P450c17 mutation H373D causing combined 17alpha-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2009;94:3089ŌĆō3092. PMID: 19470621.



47. Geller DH, Auchus RJ, Mendonca BB, Miller WL. The genetic and functional basis of isolated 17,20-lyase deficiency. Nat Genet 1997;17:201ŌĆō205. PMID: 9326943.



48. Sherbet DP, Tiosano D, Kwist KM, Hochberg Z, Auchus RJ. CYP17 mutation E305G causes isolated 17,20-lyase deficiency by selectively altering substrate binding. J Biol Chem 2003;278:48563ŌĆō48569. PMID: 14504283.


49. Fluck CE, Tajima T, Pandey AV, Arlt W, Okuhara K, Verge CF, et al. Mutant P450 oxidoreductase causes disordered steroidogenesis with and without Antley-Bixler syndrome. Nat Genet 2004;36:228ŌĆō230. PMID: 14758361.


50. Scott RR, Miller WL. Genetic and clinical features of p450 oxidoreductase deficiency. Horm Res 2008;69:266ŌĆō275. PMID: 18259105.


51. Sahakitrungruang T, Huang N, Tee MK, Agrawal V, Russell WE, Crock P, et al. Clinical, genetic, and enzymatic characterization of P450 oxidoreductase deficiency in four patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2009;94:4992ŌĆō5000. PMID: 19837910.




52. Hershkovitz E, Parvari R, Wudy SA, Hartmann MF, Gomes LG, Loewental N, et al. Homozygous mutation G539R in the gene for P450 oxidoreductase in a family previously diagnosed as having 17,20-lyase deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008;93:3584ŌĆō3588. PMID: 18559916.




53. Arlt W, Walker EA, Draper N, Ivison HE, Ride JP, Hammer F, et al. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia caused by mutant P450 oxidoreductase and human androgen synthesis: analytical study. Lancet 2004;363:2128ŌĆō2135. PMID: 15220035.


54. Huang N, Pandey AV, Agrawal V, Reardon W, Lapunzina PD, Mowat D, et al. Diversity and function of mutations in p450 oxidoreductase in patients with Antley-Bixler syndrome and disordered steroidogenesis. Am J Hum Genet 2005;76:729ŌĆō749. PMID: 15793702.



55. Fukami M, Nishimura G, Homma K, Nagai T, Hanaki K, Uematsu A, et al. Cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase deficiency: identification and characterization of biallelic mutations and genotype-phenotype correlations in 35 Japanese patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2009;94:1723ŌĆō1731. PMID: 19258400.



56. Krone N, Reisch N, Idkowiak J, Dhir V, Ivison HE, Hughes BA, et al. Genotype-phenotype analysis in congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to P450 oxidoreductase deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2012;97:E257ŌĆōE267. PMID: 22162478.



Fig.┬Ā1
Simplified scheme of adrenal steroidogenesis. AKR, aldo-keto reductase; Cyt.b5, cytochrome b5; P450scc, cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme; P450c17, 17╬▒-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase; 3╬▓HSD2, 3╬▓-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2; P450c21, 21-hydroxylase; P450c11AS, aldosterone synthase; P450c11╬▓, 11╬▓-hydroxylase; POR, P450 oxidoreductase; StAR, steroidogenic acute regulatory protein; SULT2A1, sulfotransferase; 18OHCort, 18-hydroxycorticosterone.
Table┬Ā1.
Characteristics of different forms of congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH)
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 16 Crossref
- Scopus
- 11,720 View
- 221 Download





